Вступ
Невралгія трійчастого нерва — поширене тяжке захворювання з класичною та атиповою формами, що є складним для лікування [12]. Щонайменше третина випадків хвороби характеризується рефрактерністю до рекомендованого лікування, яке включає здебільшого антиконвульсанти і антидепресанти різних фармакологічних груп. У таких пацієнтів значно звужується діапазон соціальної адаптації та погіршується якість життя у зв’язку з щоденним інтенсивним, виснажуючим невропатичним болем та побічними ефектами від медикаментозної терапії.
Сучасна класифікація тригемінальної невралгії згідно з The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition (ICHD-3) робить акцент на гетерогенності цього патологічного стану. S. Handa зі співавт. наводять класифікацію больових синдромів у зоні іннервації трійчастих нервів за ICOP у першій редакції, що включає власне тригемінальну невралгію (TN), burning mouth syndrome (BMS), персистуючий ідіопатичний лицевий біль (PIFP) та посттравматичний тригемінальний нейропатичний біль (PTTNP) [19].
13.1 Pain attributed to a lesion or disease of the trigeminal nerve
13.1.1 Trigeminal neuralgia
13.1.1.1 Classical trigeminal neuralgia
13.1.1.1.1 Classical trigeminal neuralgia, purely paroxysmal
13.1.1.1.2 Classical trigeminal neuralgia with concomitant continuous pain
13.1.1.2 Secondary trigeminal neuralgia
13.1.1.2.1 Trigeminal neuralgia attributed to multiple sclerosis
13.1.1.2.2 Trigeminal neuralgia attributed to spaceoccupying lesion
13.1.1.2.3 Trigeminal neuralgia attributed to other cause
13.1.1.3 Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia
13.1.1.3.1 Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia, purely paroxysmal
13.1.1.3.2 Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia with concomitant continuous pain
13.1.2 Painful trigeminal neuropathy
13.1.2.1 Painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to herpes zoster
13.1.2.2 Trigeminal post-herpetic neuralgia
13.1.2.3 Painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy
13.1.2.4 Painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to other disorder
13.1.2.5 Idiopathic painful trigeminal neuropathy
Одна із вагомих причин класичної невралгії трійчастого нерва зараз з’ясована і полягає у компресії, обумовленій нервово-судинним конфліктом [15]. Виконання декомпресивного хірургічного втручання дозволяє позбавити болю або покращити контроль над ним [32]. Натомість механізми розвитку атипової тригемінальної невралгії (згідно з попередньою класифікацією головного болю ICHD-2) у багатьох випадках, а саме із супутнім постійним болем, післягерпетичної невралгії та нейропатії трійчастого нерва, все ще залишаються остаточно нез’ясованими, що зумовлює встановлення діагнозу так званої ідіопатичної тригемінальної невралгії і звужує застосовувану терапевтичну стратегію до симптоматичної анальгетичної терапії, яка характеризується обмеженою клінічною ефективністю та низкою побічних ефектів.
Докази, накопичені протягом останніх десятиріч, вказують, що однією з причин так званої пост-герпесзостер-нейропатії, післягерпетичної невралгії, ідіопатичної тригемінальної невралгії може бути реактивована герпесвірусна інфекція [1]. Зокрема, на це вказує сучасний досвід діагностики і лікування оперізуючого герпесу і постгерпетичної невралгії після гострого тригемінального гангліорадикулоневриту [25], так само як і нещодавне з’ясування етіологічної ролі вірусу простого герпесу 1-го типу у генезі невриту лицьового нерва [8], що привертає увагу до можливості асоціації атипової невралгії трійчастого нерва з герпесвірусними інфекціями. Водночас наші спостереження за хворими з невралгією трійчастого нерва вказують, що у багатьох випадках больовому синдрому передували прояви герпесвірусної інфекції, зокрема типові висипання на губах, шкірі та слизових оболонках, періодичний або персистуючий субфебрилітет, лімфаденопатія, прояви синдрому хронічної втоми та характерні зміни на МРТ головного мозку [1, 45].
Зв’язок між герпесвірусними інфекціями і розвитком тригемінальної невралгії є складним і може включати низку різних патогенетичних механізмів, які можна розділити за природою на прямі і непрямі.
Прямі вірус-індуковані механізми формування тригемінальної невралгії пов’язані з безпосереднім ураженням системи трійчастого нерва герпесвірусом, як це відбувається при гострому гангліорадикулоневриті в гасеровому вузлі при реактивації вірусу Varicella zoster (VZV) із латентного стану [25]. Слід враховувати випадки zoster sine herpete, які становлять щонайменше 10–20 % усіх епізодів оперізуючого герпесу, через які постгерпетичну невралгію можна помилково розцінити як ідіопатичний біль в ділянці обличчя [25, 28, 58]. D.H. Gilden зі співавт. описали хронічний гангліоніт гасерового вузла VZV-етіології як причину рефрактерної тригемінальної невралгії [16]. Натомість F. Ramos зі співавт. повідомили про гостру сенсорну нейропатію, викликану VZV, як причину стійкого больового синдрому [40]. Відповідно до цього D.Y. Liu зі співавт. рекомендують застосовувати узагальнюючий термін herpes zoster-related trigeminal neuralgia для позначення всіх форм ураження системи трійчастого нерва VZV-етіології [26]. Однак герпесвіруси інших видів можуть індукувати розвиток тригемінальної невралгії/нейропатії за механізмом прямого пошкодження. Так, G.B. Krohel зі співавт. ще в 1976 році описали хронічну HSV-1-індуковану (Herpes simplex virus, HSV, вірус простого герпесу) нейропатію трійчастого нерва [23]. Пізніше W.H. Stalker зі співавт. доповіли про стійкий лицьовий біль при невпинно рецидивуючому орофаціальному герпесі, зумовленому HSV-1/2 [50]. Відповідно до цього, E. Roullet зі співавт. надали опис клінічної та патоморфологічної картини мультифокальної нейропатії, викликаної цитомегаловірусом (СMV), в імунокомпрометованих пацієнтів [41]. R.M. Farahani зі співавт. доповіли про тяжкий тригемінальний трофічний синдром в імунокомпрометованого пацієнта з невпинно рецидивуючими виразками слизової оболонки ротової порожнини СMV-етіології [14]. K. Hüfner зі співавт. вперше продемонстрували, що ДНК HHV-6 (Human herpesvirus 6, герпесвірус людини 6-го типу) поряд з нуклеїновими кислотами альфа-герпесвірусів у великій кількості присутня в сенсорних нервових гангліях краніальних нервів [20]. Ці дані підтверджуються результатами останнього патоморфологічного дослідження, проведеного I. Ptaszyńska-Sarosiek зі співавт., причому, за даними цієї роботи, ДНК HHV-6 була виявлена в нейронах сенсорних гангліїв краніальних нервів навіть частіше, ніж ДНК HSV-1 і VZV [39].
Зараз активно обговорюються непрямі механізми розвитку тригемінальної невралгії при реактивації герпесвірусів в організмі людини, до яких можна віднести компресійні, ішемічні, автоімунні та нейродегенеративні ураження. Встановлено гетерогенність таких механізмів, що включають індукцію автоімунних реакцій до мієліну та нейронів, розвиток вірус-індукованих васкулопатій з ішемічним ураженням структур трійчастих нервів, тромбоз кавернозного синуса в зоні анатомічного проходження трійчастого нерва, розвиток вірус-асоційованих пухлин та псевдопухлинних інфільтративних уражень з вторинним залученням волокон трійчастих нервів у різних анатомічних зонах, а також порушення механізмів центральної регуляції болю, включаючи дані щодо зв’язку між HHV-6 та розвитком скроневого медіанного склерозу ЦНС [10, 33, 42]. Так, підтверджуючи асоціацію рефрактерного болю в обличчі з розсіяним склерозом, C.M.F. Li зі співавт. пропонують розділяти так звану класичну тригемінальну невралгію (CTN) та тригемінальну невралгію, вторинну щодо розсіяного склерозу (MSTN), як різні нозології [24]. Ураження структур мезолімбічної системи головного мозку, яке відбувається при вірус-індукованому скроневому медіанному склерозі [55] або автоімунних лімбічних енцефалітах, зумовлених автоантитілами до автоантигенів нейронів гіпокампів [17], може призводити до порушення механізмів центральної регуляції болю при тригемінальних невралгіях у людей. Описані випадки стійкої тригемінальної невралгії компресійного генезу, зумовленої EBV-індукованими пухлинами, зокрема інтракраніальною лейоміомою [43], неоплазією із гладеньких міоцитів кавернозного синуса [56] та В-клітинним лімфоматоїдним гранулематозом [49]. Натомість M. Adachi доповів про псевдотуморозне інфільтративне ураження язикоглоткового і блукаючого нервів VZV-етіології з клінічною картиною рефрактерного болю в ділянці обличчя [2]. Відомі описи стійких лицьових больових синдромів унаслідок ішемічного ураження трійчастих нервів при тромбозі артерій, що живлять ці краніальні нерви, при VZV-індукованих васкулопатіях [33].
Отже, сучасний аналіз зв’язків між реактивованими герпесвірусними інфекціями та тригемінальною невралгією має здійснюватися комплексно, з урахуванням усього відомого нині спектра прямих і непрямих шляхів ураження системи тригемінальних нервів при реактивації герпесвірусів із стану латентності або персистенції в імунокомпрометованих пацієнтів.
Подальші дослідження цих асоціацій відкрили б шлях до заснованого на етіології клінічного діагнозу і застосування етіотропного противірусного лікування при рефрактерній атиповій невралгії, асоційованій з герпесвірусними інфекціями, або при рецидивах після хірургічного лікування нервово-васкулярних конфліктів у зоні трійчастих нервів, дозволивши покращити контроль над тяжким інвалідизуючим болем у пацієнтів зі стійкими формами алгічних феноменів в обличчі, пов’язаними з герпесвірусними агентами.
Мета роботи: провести діагностику реактивованих герпесвірусних інфекцій у пацієнтів з рефрактерною атиповою тригемінальною невралгією (13.1.1.1.2; 13.1.1.2.3; 13.1.1.3.2; 13.1.2.2; 13.1.2.4; 13.1.2.5 за ICHD-3) з оцінкою відомих патогенетичних зв’язків між больовим феноменом і мікробним агентом та вивченням ефективності і безпечності комбінованого противірусного лікування.
Завдання дослідження:
1. Провести діагностику реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції у пацієнтів з атиповою рефрактерною невралгією трійчастого нерва.
2. Здійснити пошук можливих шляхів впливу реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції на атипову рефрактерну тригемінальну невралгію.
3. Оцінити імунний статус пацієнтів з атиповою рефрактерною тригемінальною невралгією, асоційованою з реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією.
4. Апробувати комбіновану противірусну терапію із застосуванням валацикловіру і рекомбінатного альфа2b-інтерферону у пацієнтів з атиповою рефрактерною тригемінальною невралгією, асоційованою з реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією.
Матеріали та методи
Для досягнення поставленої мети було проведене проспективне контрольоване нерандомізоване клінічне дослідження за участю 95 пацієнтів з ідіопатичною рефрактерною атиповою тригемінальною невралгією за період з 2012 до 2021 р., яке стало результатом тісного співробітництва відділення субтенторальної нейроонкології Інституту нейрохірургії імені академіка А.П. Ромоданова НАМН України, Інституту імунології та алергології та Інституту експериментальної і клінічної медицини Національного медичного університету імені О.О. Богомольця, відділів нейроімунології та нейробіохімії Інституту нейрохірургії імені академіка А.П. Ромоданова НАМН України (рис. 1).
/8.jpg)
Критеріями включення пацієнта у дослідження були атиповий характер тригемінальної невралгії, висока або середня інтенсивність невропатичного болю, тривалість хвороби більше 1 року, рефрактерність до рекомендованих знеболюючих засобів та верифікована лабораторними методами герпесвірусна інфекція. Критеріями виключення були відмова пацієнта від участі у дослідженні, задіяність в інших випробуваннях, одонтогенний генез невралгії нейропатії, відсутність належного комплаєнсу з дослідниками, поява побічних ефектів апробовуваних ліків, що потребували їх відміни, розвиток інших хвороб під час участі у дослідженні, з приводу яких призначали додаткове лікування, а також прийом медичних препаратів за іншими показаннями. Кінцевими точками дослідження виступали інтенсивність невропатичного болю, визначена суб’єктивним способом на підставі даних візуальної аналогової шкали (ВАШ), величина вірусного навантаження за даними ПЛР сироватки крові (за виключенням інфекцій, викликаних вірусами герпесу 1, 2 і 3-го типів) та динаміка досліджуваних імунологічних показників. У разі HSV-1/2- та VZV-інфекцій контроль стану вірусу здійснювали за результатами серологічних тестів через 2 місяці лікування (за титрами сироваткових специфічних IgM та IgA) та через 6 місяців від початку терапії (за титром сироваткових специфічних IgG).
Вік пацієнтів коливався від 25 до 47 років, у середньому 35,0 ± 5,1 року. Тривалість невралгії до початку участі особи у дослідженні становила від 2 до 16 років, у середньому 5,20 ± 0,41 року. Жінки становили 84 % учасників дослідження.
Дослідження проводилося наступним чином. Спочатку пацієнтів з різних регіонів України направляли неврологи і нейрохірурги до спеціалістів центру лікування болю, де встановлювався або підтверджувався діагноз атипової рефрактерної тригемінальної невралгії. Пацієнти з виявленими новоутвореннями в дослідження не входили.
Тих осіб, що дали добровільну інформовану згоду на участь у клінічному випробуванні, направляли до відділів нейроімунології та нейробіохімії Інституту нейрохірургії для проходження запланованих лабораторних тестів з метою ідентифікації герпесвірусної інфекції (рис. 1). У подальшому брали участь у дослідженні тільки ті пацієнти, у яких відзначалися лабораторні ознаки реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції. Ці учасники увійшли до групи спостереження (n = 95). Надалі пацієнти консультувалися й обстежувалися в Інститутах імунології та алергології та експериментальної і клінічної медицини, де їм проводили поглиблену оцінку імунного статусу і призначали апробовувану комбіновану противірусну терапію. Лікування проводили на підставі наявності реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції, що, згідно з міжнародною клінічною практикою, підлягає терапії. Через 1 і 2 місяці від початку терапії пацієнти проходили контрольні дослідження вірусного навантаження та імунного статусу. Повний курс двомісячної терапії і спостереження пройшли 64 пацієнти. Вони становили досліджувану групу (ДГ; n = 64). Інші хворі або відмовилися від лікування, або не дотримувалися призначеної схеми терапії, що могло суттєво вплинути на отримані результати. Ці пацієнти становили контрольну групу 1 (КГ1; n = 31), дані якої порівнювали з такими у групі дослідження. Таким чином з’ясовувалася ефективність апробованої терапії порівняно з природним перебігом хвороби. Також набрали КГ2, яку становили 32 пацієнти загальної популяції порівнянного віку та статі, які не страждали на тригемінальну невралгію.
Реактивовану вірусну інфекцію діагностували на підставі результатів ПЛР лейкоцитів крові з видоспецифічними праймерами герпесвірусів (HSV-1/2, VZV, EBV (вірус Епштейна — Барр), CMV, HHV-6, –HHV-7, HHV-8). Використовували реактиви виробників «ДНК-Технологія», «АмпліСенс» (для HSV-1/2, VZV, EBV, CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7) і «Біоком» (для HHV-7). Беручи до уваги відмінності у властивостях збудників і патогенезі викликаної ними інфекції, проводили також визначення сироваткової концентрації IgM, IgA та IgG до HSV-1/2 та VZV за допомогою твердофазного імуноферментного аналізу («Вектор-Бест», РФ).
Поглиблене імунологічне обстеження включало вивчення показників загального аналізу крові, субпопуляційного складу лімфоцитів з використанням лазерної проточної цитофлуориметрії (цитофлуориметр «Epics Xl», США) і методу непрямої імунофлуоресценції з моноклональними антитілами до CD-маркерів з двома або трьома мітками (CD3+, CD3+CD4+, CD3+CD8+, CD3–CD19+, CD3–CD16+CD56+, CD3+CD16+CD56+) (реактиви «Beckman Coulter», США). Фагоцитоз оцінювали за даними латекс-тесту з визначенням показника фагоцитозу, фагоцитарного індексу, кількості активних фагоцитів і фагоцитарної ємності крові, а також за активністю мієлопероксидази фагоцитів (лазерна проточна цитофлуориметрія). Сироваткові концентрації імуноглобулінів основних класів (М, G, А) визначали за результатами простої радіальної імунодифузії за Манчіні. Концентрацію IgE та IgD у сироватці крові вимірювали за допомогою імуноферментного аналізу («Вектор-Бест», РФ). Додатково визначали вміст субкласів IgG (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4) методом імуноферментного аналізу.
Оцінювали результати серологічних досліджень сироватки крові на предмет виявлення специфічних антинейрональних автоантитіл до автоантигенів гіпокампів, які валідовані зараз як лабораторні маркери автоімунних лімбічних енцефалітів у дітей і дорослих, а саме автоантитіл до глутамінокислої декарбоксилази (GADA), калієвих каналів нейронів, амфіфізину, NMDA-рецепторів нейронів, GABA, СV2, Yo, Rі, Ма, Hu, AMPAR 1 і 2 (ELISA; «MDI Limbach Berlin GmbH», Німеччина), що відповідає підходам до діагностики автоімунних лімбічних енцефалітів у людей [16].
Усім пацієнтам виконували МРТ головного мозку із програмою CISS3D чи 3Ddrive прицільно на зону корінців V черепних нервів [45]. Оцінювали нейрорадіологічні ознаки ранньої демієлінізації в режимі T1-w/T2-w при діагностиці тригемінальної невралгії у пацієнтів з розсіяним склерозом, як це рекомендують C.M.F. Li зі співавт. [24].
Апробовувана схема комбінованої противірусної терапії відповідала загальноприйнятим підходам до лікування реактивованих герпесвірусних інфекцій і включала валацикловір per os у дозі 3 г/день, розділеній на три прийоми по 1 г кожні 8 годин, і рекомбінантний альфа2b-інтерферон у дозі 3 млн МО п/шк 1 раз на 2 доби ввечері протягом 2 місяців поспіль.
Для статистичного аналізу отриманої інформації застосовували методи структурного та порівняльного аналізів. Для вивчення розподілу варіантів у варіаційному ряду використовували тест Shapiro-Wilk. З метою встановлення вірогідності відмінностей результатів застосовували T-критерій Стьюдента з розрахунком коефіцієнта довірчої ймовірності р (параметричний критерій) і числа знаків Z за Ю.В. Урбахом (непараметричний критерій).
Дослідження виконувалось як фрагмент наукової роботи на замовлення МОЗ України, грант № 0118U001218. Протокол № 128 від 23.12.2019 року Комісії з біоетики НМУ імені О.О. Богомольця.
Результати та обговорення
Рефрактерна атипова тригемінальна невралгія виявилася тісно асоційованою з реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією, оскільки останню вдалося виявити у 87 % обстежених, які відповідали критеріям дослідження, тоді як у пацієнтів без тригемінальної невралгії з КГ2 — тільки в 23 % випадків (р < 0,05; Z < Z0,05).
У цілому в ДГ VZV-інфекція була ідентифікована у 33 %, HSV-1/2 — у 23 %, EBV — у 26 %, СMV — у 7 %, HHV-6 — у 25 %, HHV-7 — у 42 %, HHV-8 — у 2 % випадків. Моноінфекція мала місце у 42 %, а мікстінфекція — у 58 % випадків (рис. 2).
Нами проведений доступний аналіз можливих сполучних ланок патогенезу між наявними атиповою тригемінальною невралгією і реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією у пацієнта в кожному конкретному випадку.
Встановлено, що у деяких пацієнтів мала місце постгерпетична невралгія після фаціального оперізуючого герпесу в режимі zoster sine herpete (17 % випадків). Типова екзантема — наріжний камінь клінічної діагностики герпетичного ганліорадикулоневриту, однак у 10–20 % випадків реактивація VZV із гасерового вузла трійчастого нерва не супроводжується шкірними висипаннями, що може обумовити діагностичні помилки [58]. Ідентифікація ДНК вірусу у слині, виявлення специфічних IgM, IgA в крові або вірогідного приросту титру сироваткових специфічних IgG (метод парних сироваток) дозволяли провести правильну диференціальну діагностику між постгерпетичною невралгією та ідіопатичною тригемінальною невралгією в таких випадках.
Ще у 23 % випадків виявили ДНК HSV-1/2 в слині методом ПЛР, специфічні IgM, IgA до HSV-1/2 у крові, що, зважаючи на відсутність екза- та енантеми, було розцінено як прояв herpes sine herpete. Зараз накопичено низку повідомлень про можливість розвитку тригемінальної невралгії при реактивованій HSV-1/2-інфекції орофаціальної локалізації [23, 50].
У 16 % випадків лобноскроневий біль був причиною VZV-індукованої дифузної васкулопатії дрібних церебральних артерій (термін запропонований M.A. Nagel зі співавт. [33]) з множинними лакунарними інфарктами в субкортикальних ділянках білої речовини півкуль великого мозку в зоні кровопостачання середньої мозкової артерії. Зони лакунарних церебральних інфарктів було виявлено за допомогою МРТ головного мозку в конвенційних режимах (рис. 3). Відзначалися специфічні IgM та IgA до VZV у сироватці крові. У половині випадків здійснено люмбальну пункцію і виявлено феномен інтратекального синтезу специфічних IgG до VZV. У таких випадках припускали ішемічний характер тригемінальної невралгії внаслідок тромбозу живлячої артерії, як це постулюється при множинному мононевриті краніальних нервів VZV-етіології [33].
/9_2.jpg)
У 27 % випадків за даними МРТ відзначалися випадки скроневого медіанного склерозу, причому у таких пацієнтів відзначалися переважно реактивовані –HHV-6- і HHV-7-інфекції. На сьогодні встановлено, що HSV-1/2 і HHV-6 можуть здійснювати трансольфакторну міграцію зі слизової оболонки носової порожнини до структур мезолімбічної системи скроневих часток півкуль великого мозку (гіпокампів, мигдалеподібних тіл, острівців, парагіпокампальних звивин), індукуючи розвиток нейродегенеративного ураження за типом скроневого медіанного склерозу [52] (рис. 4). Результати нещодавнього метааналізу контрольованих клінічних досліджень підтверджують асоціацію HHV-6 і скроневого медіанного склерозу у людей [55]. C. Rusbridge у відповідному систематичному огляді вказує, що порушення центральної регуляції болю при ураженні кортиколімбічної системи ЦНС (префрональної кори, гіпокампів, мигдалеподібних тіл) є одним із типових механізмів формування рефрактерних больових синдромів [42]. J. Alper зі співавт., використовуючи МР-томографи з величиною магнітної індукції котушки в 7 Тл, показали прогресуюче зменшення об’єму мигдалеподібних тіл у пацієнтів з рефрактерними тригемінальними невралгіями — феномен, типовий для скроневого медіанного склерозу у людей [4]. W. Liu зі співавт. показали, що зниження активності МАРК-асоційованого активаційного шляху сприяє зменшенню інтенсивності болю при тригемінальній невралгії [26]. Водночас E. Engdahl зі співавт. продемонстрували, що HHV-6 індукує розвиток скроневого медіанного склерозу шляхом аномальної гіперактивації МАРК-асоційованого активаційного шляху контролю інтенсивності запалення та апоптозу в паренхімі ЦНС [13].
У 21 % випадків діагностовано ремітуюче-рецидивну форму розсіяного склерозу з урахуванням даних МРТ головного мозку з контрастом. Відзначалася демієлінізація у проксимальному відділі трійчастого нерва поблизу виходу його зі стовбура мозку. У більшості цих пацієнтів не відзначалося інших неврологічних проявів розсіяного склерозу на момент звернення, окрім невропатичного болю в обличчі, незважаючи на наявність множинних перивентрикулярних вогнищ демієлінізації на нейровізуалізаційних знімках (рис. 5), що зумовлювало помилкове клінічне діагностування ідіопатичної атипової тригемінальної невралгії. Результати останніх метааналізів і систематичних оглядів рандомізованих контрольованих клінічних досліджень підтверджують асоціацію розсіяного склерозу з EBV- [21] і HHV-6-інфекціями [38]. У осіб цієї підгрупи відзначалися реактивовані EBV-, HHV-6-, HHV-7-інфекції, що узгоджується з усталеними уявленнями про роль цих опортуністичних вірусних агентів як основних тригерів розсіяного склерозу у людей. Нещодавно C.M.F. Li зі співавт. у спеціально спланованому дослідженні валідували нейрорадіологічні ознаки ранньої демієлінізації в T1-w/T2-w режимах для правильної діагностики початкових проявів розсіяного склерозу у пацієнтів з рефрактерним нейропатичним болем у ділянці обличчя як ізольованим клінічним синдромом [24]. Ґрунтовний систематичний огляд з проблеми нейропатичних болів при розсіяному склерозі підготовлено N.N. Spirin зі спів–авт. [48].
/10.jpg)
У 19 % випадків мав місце автоімунний лімбічний енцефаліт, зумовлений автоантитілами до автоантигенів нейронів гіпокампів, зокрема до GADA, калієвих каналів нейронів, амфіфізину та молекули СV2. У таких випадках переважали реактивовані EBV-, HHV-6-, HHV-7-інфекції. Зараз встановлено, що герпесвіруси, так само як і злоякісні новоутворення, можуть бути тригерами автоімунних лімбічних енцефалітів у людей [53], що можуть призводити до порушення центральних механізмів ноцицепції і проявлятися у вигляді феномена рефрактерного болю в обличчі. Так, P. Schwenkenbecher зі співавт. в спеціально спланованому клінічному дослідженні показали, що інтратекальний синтез специфічних IgG до EBV при верифікованих автоімунних лімбічних енцефалітах відзначався в 19 % випадків, тоді як при розсіяному склерозі — лише в 7 % випадків [44]. У половині зареєстрованих нами випадків автоімунних енцефалітів МРТ головного мозку в конвенційних режимах не демонструвала типового феномена гіперінтенсивності сигналу від гіпокампів в Т2-зваженому режимі та режимі FLAIR (рис. 6), що вказувало на те, що мали місце так звані автоімунні лімбічні енцефаліти з нормальною МР-картиною (термін запропонували M. Guasp зі співавт. [17]), хоча клінічні, серологічні та нейрофізіологічні дані (рис. 7) вказували саме на цей діагноз. Тому початково таким пацієнтам встановлювали помилковий діагноз за превалюючим клінічним проявом — рефрактерним болем у ділянці обличчя.
У більшості пацієнтів ДГ відзначалися нейрорадіологічні ознаки девіації, деформації корінця трійчастого нерва на боці больового синдрому в парамостовій цистерні порівняно зі здоровою стороною, хоча МРТ-ознаки судинної компресії трійчастого нерва при поглибленому нейрорадіологічному обстеженні було виявлено тільки в 17 % випадків, однак у них парадоксально не відзначалося клінічної картини типової невралгії, що зумовлювало включення цих пацієнтів до даного дослідження за критерієм атиповості алгічного феномена. При проведенні нейрохірургічного втручання було виявлено ознаки хронічного запалення і спайки в ділянці нервово-судинного конфлікту, що дозволило нам припустити, що саме реактивована герпесвірусна інфекція і була причиною формування запалення, що поглибило вже існуючий конфлікт між судиною і нервом (рис. 8).
/11.jpg)
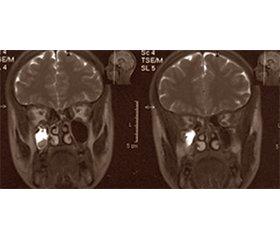
У 13 % випадків біль у середній частині обличчя пов’язали з продуктивним полісинуситом з формуванням гранульом, псевдополіпів і кіст, наповнених серозним умістом (рис. 9). Поруч розташований трійчастий нерв, найбільш ймовірно, залучався вторинно внаслідок поширення локального патологічного процесу. У деяких таких хворих у минулому на тлі атипової невралгії або навіть до моменту її виникнення відзначалися епізоди гострого пронизуючого болю з ринореєю, пов’язані зі спонтанним розривом зазначених кіст. Такі ураження досить поширені у популяції, однак зазвичай не проявляються клінічно і нерідко є випадковою знахідкою при проведенні МРТ головного мозку з інших причин. Наш досвід діагностики свідчить про можливий зв’язок з місцевою герпесвірусною інфекцією на тлі імунних дисфункцій, що сприяють формуванню так званого холодного запалення. Справді, у цих випадках діагностовано переважно ізольований дефіцит IgE та дефіцит мієлопероксидази фагоцитів, при яких описані випадки індукції вогнищ холодного запалення у верхніх дихальних шляхах і додаткових пазухах носа [34, 47]. Досі опубліковано обмаль інформації про гіперпластичні продуктивні синусити герпесвірусної етіології. Зокрема, A. Gujadhur зі співавт. повідомили про тяжкий гіперпластичний синусит, викликаний CMV, у ВІЛ-негативного реципієнта алогенної нирки [18].
/12.jpg)
У 8 % пацієнтів з невропатичним болем у зоні іннервації ІІІ гілки трійчастого нерва діагностовано цервікогенну краніалгію, що імітувала тригемінальну невралгію шляхом іррадіації больових відчуттів уздовж комунікацій між шийним відділом спинного мозку і трійчастими нервами [15]. Проблема цервікогенної цервікалгії як причини помилкової діагностики невралгії трійчастого нерва детально розглянута в систематичному огляді N. Bogduk зі співавт. [8]. У їхнїх пацієнтів мали місце підвивихи у фасеткових суглобах між 2-м і 3-м шийними хребцями з вторинними реактивними змінами, у зв’язку з чим пацієнти потребували виконання ортопедичних хірургічних втручань. Як відомо, біль може мігрувати з цервікального відділу хребта до зони тригемінальної іннервації на обличчі за посередництва анастомозів між гілками перших трьох шийних нервів і нижньої гілкою трійчастого нерва на периферії або на сегментарному рівні завдяки продовженню цервікального ядра трійчастого нерва у верхніх шийних сегментах спинного мозку. L.B. Mitrofanova зі співавт. описали випадки міжхребцевих дисцитів –HSV-1- і –HSV-2-етіології [31], однак також відомо, що у разі реактивованої інфекції знижується поріг ноцицепції через запальну реакцію, що могло відігравати роль в індукції проєкційного болю в обличчі [54].
У 6 % випадків після проведення прицільної нейровізуалізації виявлено перенесений тромбоз кавернозного синуса, що розцінено як безпосередня причина атипового невралгічного болю. Біль відзначався у зоні іннервації І гілки трійчастого нерва, що топічно відповідало наявному тромбозу. Тромбоз венозних синусів мозку описаний як можливе ускладнення реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції в низці наукових публікацій. Так, J. Chan зі співавт. діагностували гострий тромбоз латерального венозного синуса мозку у пацієнта з zoster sine herpete [11]. R. Pazos-Añón зі співавт. виявили венозний церебральний тромбоз у ВІЛ-інфікованого хворого з синдромом Рамсея Ханта [35].
Ще в 5 % мав місце шийний менінгорадикуліт HHV-7-етіології, на що вказувало відповідне накопичення гадолінію на посилених контрастом МР-знімках в Т1-зваженому режимі. Раніше C.M. Miranda зі співавт. повідомляли про можливість розвитку менінгомієлітів під час реактивації HHV-7 з формуванням невропатичного болю [30]. Розвиток болю в обличчі пояснюється зворотною міграцією больових відчуттів з шийних нервів до мандибулярної гілки трійчастого нерва через периферичні комунікації або через цервікальне ядро трійчастого нерва, представлене в верхніх цервікальних сегментах спинного мозку.
У 3 % випадків біль в обличчі асоціювався з гранульомою в ділянці корінця трійчастого нерва VZV-етіології (рис. 10). Як стало відомо завдяки численним повідомленням, герпесвіруси можуть ставати причиною гранулематозного процесу, що отримав назву псевдопухлини [2]. Тригемінальна невралгія також може бути проявом істинної пухлини мостомозочкового кута, що подібна за клінічними проявами до гранульоми, у зв’язку з чим ми проводили диференціальну діагностику із застосуванням МРТ з контрастом, МР-спектроскопії, позитронно-емісійної томографії та біопсії мозку.
/13.jpg)
Під час отримання комбінованого противірусного лікування відбулося зниження інтенсивності лицьового невропатичного больового синдрому в 43 % випадків у ДГ і в жодному — у КГ1 (р < 0,05; Z < Z0,05). Повного регресування алгічного феномена досягнуто лише в 18 % випадків у ДГ і в жодному — у КГ1 (р < 0,05; Z < Z0,05). У цілому позитивний ефект досягнуто в 61 % випадків (рис. 11). Сприятливий ефект терапії розвивався вже протягом першого місяця лікування і посилювався на другому і третьому місяці участі у дослідженні. У більшості осіб з позитивною відповіддю на противірусне лікування тривалість невралгії не перевищувала 5 років. Проте в 39 % випадків в ДГ проведене противірусне лікування не вплинуло на больовий синдром. Водночас майже в половині випадків резистентності до противірусних ліків відзначався позитивний феномен відновлення чутливості до рекомендованих препаратів проти нейропатичного болю (габапентину, прегабаліну), до яких раніше спостерігалась рефрактерність.
Ефективність лікування реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції була вищою, ніж досягнутий вплив на больовий синдром. Кращі результати отримані при VZV-інфекції (72 %; р < 0,05; Z < Z0,05) і дещо гірші — при інфекціях, викликаних лімфотропними герпесвірусами (57 %; р < 0,05; Z < Z0,05), що, на нашу думку, пов’язано з відмінностями у чутливості до валацикловіру і рекомбінатного альфа-інтерферону у герпесвірусів різних підродин (рис. 12). Усунення VZV сильніше корелювало з позитивною відповіддю з боку больового синдрому, ніж пригнічення лімфотропних герпесвірусів. Побічних реакцій, окрім короткочасного грипоподібного синдрому у 53 % випадків, зареєстровано не було, що дозволяє говорити про задовільний профіль безпечності застосовуваної терапії. Застосування ацикловіру, валацикловіру і фамцикловіру стало традиційним при реактивації герпесвірусних агентів завдяки накопиченій доказовій базі ефективності [36, 51]. Так, D.H. Gilden зі співавт. описали хронічний гангліоніт, викликаний VZV, у пацієнта з персистуючим невропатичним болем. Больовий синдром вщухав повністю 5 разів поспіль після курсів фамцикловіру і закономірно відновлювався через тиждень після відміни противірусного препарату [16]. Раніше T.C. Merigan зі співавт. продемонстрували ефективність рекомбінантного альфа-інтерферону при оперізуючому герпесі і пов’язаній з ним постгерпетичній невралгії у подвійному сліпому плацебо-контрольованому випробуванні [29].
У пацієнтів ДГ після проведення оцінки імунного статусу діагностовані малі імунні дисфункції, мінорні імунодефіцити (85 % випадків, що вірогідно більше, ніж в КГ2 — 26 % випадків (р < 0,05; Z < Z0,05)), зокрема ізольовані дефіцити IgE підкласу IgG1, IgA, IgM, дефіцит мієлопероксидази фагоцитів, дефіцити природних кілерів (NK) та природних кілерних Т-клітин (NKT), ідіопатична CD4+ Т-клітинна лімфопенія (рис. 13). Нормальний імунний статус діагностовано лише у 15 % випадків у ДГ.
Усі виявлені імунні дисфункції могли бути безпосередньою причиною реактивації герпесвірусів, про що є повідомлення в науковій літературі. Так, тяжкі реактивовані герпесвірусні інфекції з формуванням органних уражень описані при дефіциті природних кілерів [7], природних кілерних Т-клітин [6], дефіциті молекули CD16 [3], ідіопатичній Т-клітинній лімфопенії [57], дефіциті підкласу IgG1 [22] та дефіциті IgE [27, 37], що траплялися серед пацієнтів, які брали участь у дослідженні.
Також про важливість діагностування імунних дисфункцій у цієї категорії пацієнтів свідчать виявлені асоціації між формою імунодефіциту, видом реактивованого вірусу і чинниками безпосереднього ураження нерва під час реактивованої інфекції. У разі реактивації VZV реєструвалися здебільшого клітинні порушення імунітету, зокрема дефіцит природних кілерів, дефіцит природних кілерних Т-клітин або дефіцит молекули СD16, що включає поєднаний дефіцит NK- і NKT-клітин. Ці дані узгоджуються з клінічними повідомленнями про спектр імунних порушень у пацієнтів з рецидивними інфекціями, викликаними альфа-герпесвірусами. У цьому контексті інформативним є фундаментальне дослідження E. Backström зі співавт., у якому показана критично важлива участь резидентних природних кілерів сенсорних нервових гангліїв у контролі над латентним VZV. Ці клітини продукують інтерферони І типу у разі спроби реактивації вірусу, справляючи віростатичний ефект і запобігаючи тим самим реактивації латентного патогену [5]. Натомість при інфекціях, викликаних лімфотропними герпесвірусними агентами, переважали порушення гуморального імунітету і фагоцитозу.
Привертає увагу велика питома вага дефіциту IgE у пацієнтів ДГ — 30 % випадків. У загальній популяції, згідно з відомими даними, питома вага дефіциту IgE не перевищує 3 %, а серед хворих з імунозалежною патологією — 12 % [46], тобто у пацієнтів з тригемінальною невралгією питома вага вказаної імунної дисфункції принаймні в 10 разів більша, ніж у загальній популяції, і майже втричі більша, ніж серед хворих осіб. Як відомо, IgE задіяний у механізмах місцевого імунітету, що може пояснити підтримання реактивованого стану герпесвірусів зниженням імунного нагляду в верхніх дихальних шляхах і прилеглих тканинах (вхідних воротах, зоні первинного афекту), де розташовується трійчастий нерв. Крім того, дефіцит IgE сприяє формуванню вогнищ так званого холодного запалення, які відзначалися у деяких пацієнтів ДГ [34]. У популяційному дослідженні за участю 18 487 осіб, проведеному E. Magen зі співавт., встановлена асоціація селективного дефіциту IgE з бронхіальною астмою і гіперреактивністю бронхів у дітей і хронічними синуситами, середнім отитом, автоімунними і онкологічними ураженнями у дорослих [27].
Висновки
Результати даного клінічного дослідження показують тісну асоціацію атипової рефрактерної тригемінальної невралгії і реактивованих герпесвірусних інфекцій. Отримані дані вказують на гетерогенність походження больового синдрому у різних пацієнтів зі спільним фенотипом алгічного синдрому. Цей фенотип може бути наслідком прямого або опосередкованого впливу реактивованих герпесвірусних інфекцій людини як на структури трійчастих нервів на периферії, так і на центри регуляції болю в ЦНС. Найчастіше фенотип рефрактерної атипової тригемінальної невралгії асоційований з реактивованими VZV- та HHV-7-інфекціями та рідше — з іншими герпесвірусними інфекціями.
У пацієнтів з атиповою рефрактерною тригемінальною невралгією, асоційованою з реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією, залучення трійчастого нерва може бути обумовлене як прямим (zoster sine herpete, herpes sine herpete, гангліоніт, неврит), так і непрямим впливом вірусу внаслідок ураження ЦНС (VZV-васкулопатія, HHV-7-менінгомієліт), компресії корінця і нервових волокон (псевдопухлини, тромбоз кавернозного синуса, продуктивний синусит), автоімунних реакцій до мієліну та нейронів (розсіяний склероз, автоімунний лімбічний енцефаліт), вірус-індукованих порушень центральних механізмів регуляції болю (скроневий медіанний склероз) та індукції системного й локального запалення з ймовірним зниженням порога ноцицепції (цервікогенна цефалгія, ускладнений судинно-васкулярний конфлікт).
У пацієнтів з фенотипом рефрактерної атипової тригемінальної невралгії, асоційованої з реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією, відзначаються малі імунні дисфункції (мінорні імунодефіцити), які стосуються клітинного природженого і гуморального адаптивного імунітету, що були пов’язані з герпесвірусною інфекцією, медикамент-індукованою імуносупресією або генетичними чинниками, виявляючись у деяких випадках у найближчих родичів пацієнтів; особливо тісною є асоціація з ізольованим дефіцитом IgE, NK- і NKT-клітин.
Комбіноване противірусне лікування, що включає валацикловір і рекомбінантний альфа2b-інтерферон, є високоефективним для усунення реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції у короткостроковій перспективі (77 %), середньої ефективності — щодо зниження інтенсивності невралгічного болю (61 %) і малоефективним для корекції імунних порушень (частковий ефект у 26 % випадків) при фенотипі рефрактерної атипової тригемінальної невралгії, асоційованої з реактивованою герпесвірусною інфекцією. Найбільша ефективність апробовуваного лікування зареєстрована у підгрупі пацієнтів, у яких відзначалася постгерпетична невралгія після zoster sine herpete та herpes sine herpete, тому це основна цільова когорта для клінічного застосування запропонованої противірусної терапії.
Необхідним є виконання більших за кількістю учасників досліджень із залученням плацебо-контролю, присвячених вивченню асоціації атипової рефрактерної тригемінальної невралгії і реактивованої герпесвірусної інфекції та оцінці ефективності і безпечності противірусного лікування в цих випадках.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автори заявляють про відсутність конфлікту інтересів та власної фінансової зацікавленості при підготовці даної статті.
Отримано/Received 20.02.2022
Рецензовано/Revised 28.02.2022
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 04.03.2022
/9.jpg)

/8.jpg)
/9_2.jpg)
/10.jpg)
/11.jpg)
/12.jpg)
/13.jpg)
/14.jpg)