Журнал «Травма» Том 25, №3, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Напружено-деформований стан надплечово-ключичного суглоба при ушкодженні зв’язок ключично-акроміального суглоба і різних способах фіксації
Авторы: Бур’янов О.А. (1), Кваша В.П. (1), Чекушин Д.А. (1), Задніченко М.О. (1), Карпінський М.Ю. (2), Яресько О.В. (2)
(1) - Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - ДУ «Інститут патології хребта та суглобів імені професора М.І. Ситенка НАМН України», м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
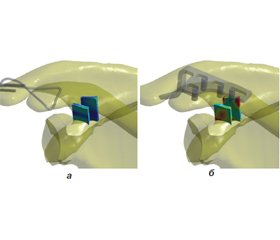
Актуальність. Існують два основних способи фіксації акроміального кінця ключиці за допомогою металевих конструкцій: гачкоподібна пластина (hook platе) і спосіб Вебера (tension band wiring). Недоліки сучасних фіксуючих конструкцій негативно впливають на результати лікування, що потребує розробки новітніх засобів для стабілізації акроміального кінця ключиці. Мета: провести порівняльний аналіз фіксації акроміального кінця ключиці за Вебером, hook platе і запропонованою конструкцією шляхом вивчення напружено-деформованого стану надплечово-ключичного суглоба при поєднаному ушкодженні lig. acromioclavicularе inferior і lig. acromioclavicularе superior і різних способах фіксації. Матеріали та методи. У даному дослідженні моделювали поєднане ушкодження зв’язок надплечово-ключичного суглоба, а саме lig. acromioclavicularе inferior і lig. acromioclavicularе superior з фіксацією акроміального кінця ключиці трьома способами: за Вебером, hook plate і запропонованою конструкцією. Використовували навантаження, які діють на надплечово-ключичний суглоб при відведенні верхньої кінцівки на кут 90°. Результати. Встановлено, що всі типи фіксаторів при ушкодженні lig. acromioclavicularе inferior і lig. acromioclavicularе superior дозволяють отримати приблизно однаковий рівень напружень у кісткових елементах моделі. Винятком є фіксація за Вебером, при якій напруження на акроміальному кінці ключиці й акроміальному виростку лопатки збільшуються в декілька разів, що може бути причиною руйнування кісткової тканини в зоні контакту з металевими елементами. Напруження в самому дроті навіть можуть перевищувати межу міцності хірургічної сталі і, як наслідок, стати причиною його розриву. Фіксатор шарнірного типу забезпечує як найкращий розподіл напружень у кісткових елементах моделі, так і досить низькій рівень напружень у неушкоджених зв’язках. З точки зору величин напружень в елементах моделі hook plate має непогані показники при відокремлених ушкодженнях зв’язок і займає проміжне положення за всіма дослідженими показниками. За критерієм мінімізації величини відносних деформацій у зв’язках ключично-лопаткового зчленування при ушкодженні lig. acromioclavicularе inferior і lig. acromioclavicularе superior кращі результати показав метод фіксації за Вебером. Але результати дослідження розподілу напружень у даній моделі зводять нанівець переваги мінімізації деформацій неушкоджених зв’язок. Висновки. Фіксація акроміального кінця ключиці за Вебером забезпечує добрі результати з точки зору зниження рівня напружень і відносних деформацій в неушкоджених зв’язках, але призводить до підвищення в кілька разів рівня напружень на акроміальному кінці ключиці та акроміальному виростку лопатки. Рівень напружень у дроті при відведенні кінцівки при ушкодженні зв’язок ключично-акроміального з’єднання може перевищувати межу міцності, що може бути причиною розриву дроту і, як наслідок, втрати стабільності надплечово-ключичного суглоба. Фіксатор hook plate займає проміжне положення за показниками розподілу напружень у моделі, але за показником відносних деформацій у неушкоджених зв’язках показав найгірший результат. Фіксатор запропонованої конструкції забезпечує найкращий баланс як за критерієм розподілу напружень в елементах моделі, так і за величиною відносних деформацій у неушкоджених зв’язках.
Background. There are two main methods of fixing the acromial end of the clavicle with the help of metal structures: hook plate, and Weber’s technique (tension band wiring). The disadvantages of modern fixing structures negatively affect treatment outcomes, which requires the development of advanced methods to stabilize the acromial end of the clavicle. Purpose: to conduct a comparative analysis on the fixation of the acromial end of the clavicle according to Weber, using hook plate and the proposed construction by studying the stress-strain state of the suprahumeral-clavicular joint with a combined injury of the lig.acromioclaviculare inferior and lig.acromioclaviculare superior and various methods of fixation. Materials and methods. In this study, we modeled a combined injury of the ligaments of the suprahumeral-clavicular joint, namely lig.acromioclaviculare inferior and lig.acromioclaviculare superior, with fixation of the acromial end of the clavicle in three ways: according to Weber, with hook plate and the proposed construction. We used loads that act on the suprahumeral-clavicular joint when the upper extremity is abducted to an angle of 90°. Results. It was found that all types of fixators in case of damage to the lig.acromioclaviculare inferior and lig.acromioclaviculare superior allow to obtain approximately the same level of stress in the bone elements of the model. An exception is Weber’s fixation, in which the stress on the acromial end of the clavicle and on the acromion process increases several times, which can be the cause for the destruction of bone tissue in the area of contact with metal elements. The stresses in the wire itself can even exceed the strength limit of surgical steel and, as a result, cause it to break. The hinge-type fixator provides the best stress distribution, both in the bone elements of the model, and a fairly low level of stress in the intact ligaments. Hook plate, from the point of view of stress values in the elements of the model, has good indicators for isolated ligament injuries and occupies an intermediate position according to all the studied indicators. In term of the criterion of minimizing relative deformations in the ligaments of the clavicular-scapular joint in case of damage to the lig.acromioclaviculare inferior and lig.acromioclaviculare superior, the Weber fixation method showed the best outcomes. But the results of the study on stress distribution in this model negate the advantages of minimizing the deformations of the intact ligaments. Conclusions. Fixation of the acromial end of the clavicle according to Weber provides good results in terms of reducing the level of stresses and relative deformations in the intact ligaments, but leads to a severalfold increase in the level of stresses on the acromial end of the clavicle and the acromion process. The level of stresses in the wire during abduction of the limb in case of damage to the ligaments of the clavicular-acromial joint may exceed the strength limit, which may be the cause of wire breaking and, as a result, loss of stability of the suprahumeral-clavicular joint. The hook plate occupies an intermediate position in terms of stress distribution in the model, but according to the index of relative deformations in the intact ligaments, it showed the worst result. Fixator of the proposed design provides the best balance, both according to the criterion of stress distribution in the model elements and the magnitude of relative deformations in the intact ligaments.
надплечово-ключичний суглоб; зв’язки; фіксація
suprahumeral-clavicular joint; ligaments; fixation