Архів офтальмології та щелепно-лицевої хірургії України Том 1, №1, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Особливості напружено-деформованого стану системи «фіксатор — кістка» при остеосинтезі нижньої щелепи в ділянці кута фіксаторами з β-Zr-Ti-Nb сплаву
Авторы: Романова А.Ю. (1), Крищук М.Г. (2)
(1) - Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - Національний технічний університет України «Київський політехнічний інститут імені Ігоря Сікорського», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Офтальмология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
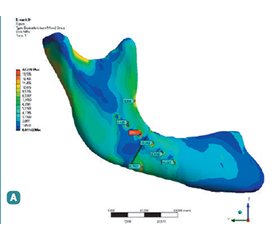
Актуальність. Переломи на ділянці кута нижньої щелепи, за даними більшості досліджень, є поширеним видом перелому, що асоціюється з найбільшою кількістю ускладнень, зокрема розвитком інфекції, уповільненням консолідації уламків та їх неправильним зрощенням, що має вторинні наслідки. Мета: порівняти вплив традиційних титанових фіксаторів для остеосинтезу нижньої щелепи і пластин з нового β-Zr-Ti-Nb сплаву на розподіл напружень і деформацій в елементах фіксації та кістковій тканині залежно від ступеня зрілості кісткового регенерату в ділянці кута нижньої щелепи. Матеріали та методи. Вивчення біомеханічної поведінки систем «фіксатор — кістка» при переломах у ділянці кута нижньої щелепи із застосуванням фіксаторів з різних матеріалів проводили в модельному експерименті, використовуючи метод імітаційного комп’ютерного моделювання. Було створено й обраховано 6 багатокомпонентних імітаційних комп’ютерних моделей зі змінними параметрами (моделі нижньої щелепи, накісткових пластин і гвинтів). Варіативними параметрами були механічні властивості елементів фіксації, що відповідали традиційному титановому сплаву Ti6Al4V (контроль) або β-Zr-Ti-Nb сплаву (основна група). Фізико-механічні параметри кісткового регенерату в моделях також змінювали, надаючи їм властивостей, притаманних: 1) незрілому фіброзно-кістковому регенерату; 2) регенерату з грубоволокнистої (ретикулофіброзної) кісткової тканини; 3) кістковому регенерату з ознаками компактизації. Результати. При застосуванні пластин з β-Zr-Ti-Nb сплаву на ділянці кута нижньої щелепи деформація системи, що характеризує стабільність фіксації, практично не відрізнялась від показників контрольної групи. Натомість розподіл напружень у системі між елементами фіксації та кістковою тканиною в зоні зрощення був більш рівномірним. Максимальні напруження в пластині в міру дозрівання регенерату зменшувались з 83,7 до 26,2 МПа і виявлялися в 1,5–2,5 раза меншими, ніж у контролі. Висновки. Проведені дослідження виявили низку біомеханічних переваг β-Zr-Ti-Nb пластин, що при правильному розташуванні дозволяють забезпечити необхідну жорсткість фіксації і водночас більшу міцність і надійність системи «фіксатор — кістка», а також наблизити розподіл функціональних навантажень у зоні кісткового зрощення до природного, притаманного ділянці кута нижньої щелепи.
Background. According to most studies, fractures in the area of the mandibular angle are a common type of injury associated with the greatest number of complications, in particular, the development of infection, slowing down the union of fragments and their incorrect fusion, which has secondary consequences. Purpose of the study: to compare the impact of traditional titanium fixators for mandibular osteosynthesis and plates made of the new β-Zr-Ti-Nb alloy on the distribution of stresses and deformations in the fixation elements and bone tissue, depending on the maturity of the bone regenerate in the area of the mandibular angle. Materials and methods. The biomechanical behavior of the fixator-bone systems in fractures in the mandibular angle area using devices made of different materials was studied through model experiments using computer simulation. Six multi-component computer models with variable parameters were created and analysed (models of the mandible, plates, and screws). The variable parameters were the mechanical properties of the fixators corresponding to traditional titanium alloy Ti6Al4V (controls) or β-Zr-Ti-Nb alloy (main group). The physical and mechanical parameters of the bone regenerate in the models were also varied by attributing them properties typical of: 1) immature fibrous bone regenerate, 2) coarse-fiber (reticulofibrous) bone regenerate, and 3) bone regenerate with signs of compaction. Results. The system’s deformation, characterizing the fixation stability, was practically indistinguishable from the indicators of the control group when using β-Zr-Ti-Nb alloy plates in the mandibular angle area. However, the distribution of stresses within the system between the fixation elements and bone tissue in the fusion zone was more uniform. The maximum stresses in the plate decreased from 83.7 to 26.2 MPa as the regenerate matured and were 1.5–2.5 times lower than in the control group. Conclusions. The conducted studies revealed several biomechanical advantages of β-Zr-Ti-Nb plates, which, when properly positioned, provide the necessary fixation rigidity, while also offering greater strength and reliability of the fixator-bone system. This also allows for a distribution of functional loads in the bone fusion zone closer to the natural one characteristic of the mandibular angle area.
остеосинтез; імітаційне комп’ютерне моделювання; нові сплави; β-Zr-Ti-Nb сплав
osteosynthesis; computer simulation; new alloys; β-Zr-Ti-Nb alloy
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- El-Anwar MW, Sweed AH. Simple percutaneous transbuccalapproach for management of mandibular angular fracture. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28:1035-1037.
- Boffano P, Roccia F, Zavattero E, et al. European Maxillofacial Trauma (EURMAT) project: a multicentre and prospective study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43:62-70.
- Al-Moraissi EA, El-Sharkawy TM, El-Ghareeb TI, Chrca–novic BR. Three-dimensional versus standard miniplate fixation in the management of mandibular angle fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43:708-716.
- Elsayed SA, Mohamed FI, Khalifa GA. Clinical outcomes of three different types of hardware for the treatment of mandibular angle fractures: a comparative retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44:1260-1267.
- Gareb B, Roossien CC, van Bakelen NB, Verkerke GJ, Vissink A, Bos RRM, van Minnen B. Comparison of the mechanical properties of biodegradable and titanium osteosynthesis systems used in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 23;10(1):18143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75299-9. PMID: 33097757; PMCID: PMC7584639.
- Gerlach KL, Erle A, Eckelt U, Loukota R, Luhr H-G, Bos RRM. 5-Surgical Management of Mandibular Fractures. In book: Brennan PA, Schliephake H, Ghali GE, Luke Cascarini L, Editors. Maxillofacial Surgery. 3rd ed. Vol. 1. Elsevier Ltd, 2017. Р. 50-73. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-7020-6056-4.00005-8.
- Niinomi M. Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2008 Jan;1(1):30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2007.07.001. Epub 2007 Aug 27. PMID: 19627769.
- Івасишин О.М., Скиба І.М., Красевська О.П., Марковський П.Є., винахідники; Інститут металофізики імені Г.В. Курдюмова НАН України, патентовласник. Біосумісний сплав із низьким модулем пружності на основі системи цирконій-титан. Патент України № 102455. 2013 Лип. 10. Бюл. № 13.
- Champy M, Loddé JP, Schmitt R, Jaeger JH, Muster D. Mandibular osteosynthesis by miniature screwed plates via a buccal approach. J Maxillofac Surg. 1978 Feb;6(1):14-21. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0503(78)80062-9. PMID: 274501.
- Маланчук В.О., Крищук М.Г., Копчак А.В. Імітаційне комп’ютерне моделювання в щелепно-лицевій хірургії: навч. посібник. Київ: Асканія, 2013. 231 с.
- Misch CE, Qu Z, Bidez MW. Mechanical properties of trabecular bone in the human mandible: implications for dental implant treatment planning and surgical placement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999 Jun;57(6):700-6; discussion 706-8. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(99)90437-8. PMID: 10368096.
- Schwartz-Dabney CL, Dechow PC. Edentulation alters material properties of cortical bone in the human mandible. J Dent Res. 2002 Sep;81(9):613-7. doi: 10.1177/154405910208100907. PMID: 12202642.