Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив прийому дієтичної добавки, що містить Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, на клінічні прояви функціональної диспепсії та якість життя пацієнтів
Авторы: Палій І.Г., Заїка С.В., Ксенчин О.О., Чернова І.В.
Вінницький національний медичний університет імені М.І. Пирогова, м. Вінниця, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
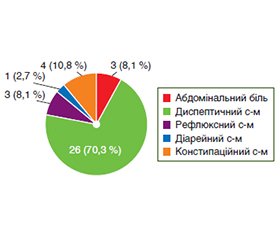
Актуальність. Функціональна диспепсія (ФД) є частим розладом, що важко піддається лікуванню та має значний негативний вплив на якість життя пацієнтів. З’являється все більше доказів того, що мікробна колонізація тонкої кишки відіграє певну роль у патофізіології ФД. Мета: вивчити вплив засобу, що містить ліофілізат молочнокислих бактерій Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strain 9702 (IMV B-7085) та продукти їх життєдіяльності, на клінічні прояви захворювання та якість життя пацієнтів з функціональною диспепсією. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження було включено 37 пацієнтів з функціональною диспепсією, середнім віком (45,9 ± 2,5) року (16 чоловіків та 21 жінка). Були проаналізовані результати опитувальника GSRS до лікування, після завершення п’ятнадцятиденного курсу прийому препарату, який містив Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, та через 15 днів після завершення курсу прийому. Динаміка якості життя оцінювалась на основі аналізу анкет SF-36, які заповнювались пацієнтами до прийому та на 30 день спостереження. Статистичні обрахунки проводились за допомогою програмного забезпечення MedCalc®, version 12.5.0.0. Результати. На 15 день прийому препарату та через 15 днів після завершення його прийому встановлено вірогідне (р < 0,05) зниження вираженості клінічних проявів згідно з опитувальником GSRS порівняно зі значенням до лікування. Аналіз динаміки відповідей на опитувальник SF-36 виявив на 30 день спостереження вірогідне підвищення (р < 0,05) рівнів усіх шкал фізичного компонента здоров’я та вірогідне підвищення (р < 0,05) рівня соціального функціонування за шкалами психологічного компонента здоров’я. Висновки. Прийом дієтичної добавки, яка містить Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strain 9702 (IMV B-7085), поліпшує клінічні прояви функціональної диспепсії, що підтверджують як зниження вираженості гастроінтестинальних симптомів, так і поліпшення якості життя у цих пацієнтів.
Background. Functional dyspepsia is a common disorder that is difficult to treat and has a significant negative impact on the quality of life of patients. There is growing evidence that small intestinal microbiota plays a certain role in the pathophysiology of functional dyspepsia. Research aim: to study the effect of a product containing lyophilized lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strain 9702 (IMV B-7085) and its metabolic products on the clinical manifestations of the disease and quality of life of patients with functional dyspepsia. Materials and methods. Thirty-seven patients (16 men and 21 women) with functional dyspepsia were included in the study, their average age was (45.9 ± 2.5) years. The score on the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale was analyzed before treatment, after completing a 15-day course of taking the probiotic additive, which contained Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, and 15 days after the end of the course. The dynamics of quality of life was evaluated based on the analysis of the SF-36 questionnaires, completed by patients before treatment and on day 30 of observation. Statistical calculations were performed using MedCalc® software, version 12.5.0.0. Results. On day 15 of taking the drug and 15 days after the end of the course, a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in the severity of clinical manifestations on the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale was found compared to the baseline. The analysis of the dynamics of responses to the SF-36 questionnaire revealed a significant increase (p < 0.05) on all scales of the physical component of health and a significant increase (p < 0.05) in social functioning on all scales of the psychological component of health on day 30 of observation. Conclusions. Taking a dietary supplement containing Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus strain 9702 (IMV B-7085) improves the clinical manifestations of functional dyspepsia, as evidenced by a reduction in the severity of gastrointestinal symptoms and increased quality of life of these patients.
функціональна диспепсія; Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus; опитувальник GSRS; оцінка якості життя
functional dyspepsia; Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus; Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale; quality of life
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Black CJ, Paine PA, Agrawal A et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the management of functional dyspepsia. Gut. 2022 Sep;71(9):1697-1723. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327737. Epub 2022 Jul 7. PMID: 35798375; PMCID: PMC9380508.
- Ford AC, Mahadeva S, Carbone MF, Lacy BE, Talley NJ. Functional dyspepsia. Lancet. 2020 Nov 21;396(10263):1689-1702. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30469-4. Epub 2020 Oct 10. PMID: 33049222.
- Wauters L, Dickman R, Drug V et al. United European Gastroenterology (UEG) and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility (ESNM) consensus on functional dyspepsia. United European Gastroenterol J. 2021 Apr;9(3):307-331. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12061. PMID: 33939891; PMCID: PMC8259261.
- Farcas RA, Grad S, Grad C, Dumitrașcu DL. Microbiota and Digestive Metabolites Alterations in Functional Dyspepsia. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2024 Mar 29;33(1):102-106. doi: 10.15403/jgld-5024. PMID: 38386888.
- Brown G, Hoedt EC, Keely S et al. Role of the duodenal microbiota in functional dyspepsia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022 Nov;34(11):e14372. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14372. Epub 2022 Apr 11. PMID: 35403776; PMCID: PMC9786680.
- Zhou L, Zeng Y, Zhang H, Ma Y. The Role of Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Functional Dyspepsia: A Review. Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 8;13:910568. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.910568. PMID: 35755434; PMCID: PMC9214042.
- Tziatzios G, Gkolfakis P, Papanikolaou IS et al. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Functional Dyspepsia. Microorganisms. 2020 May 8;8(5):691. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8050691. PMID: 32397332; PMCID: PMC7285034.
- Gao K, Mu CL, Farzi A, Zhu WY. Tryptophan Metabolism: A Link Between the Gut Microbiota and Brain. Adv Nutr. 2020 May 1;11(3):709-723. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz127. PMID: 31825083; PMCID: PMC7231603.
- Ianiro G, Pizzoferrato M, Franceschi F, Tarullo A, Luisi T, Gasbarrini G. Effect of an extra-virgin olive oil enriched with probiotics or antioxidants on functional dyspepsia: a pilot study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(15):2085-90. PMID: 23884830.
- Drago L, Meroni G, Pistone D et al. Evaluation of main functional dyspepsia symptoms after probiotic administration in patients receiving conventional pharmacological therapies. J Int Med Res. 2021 Jan;49(1):300060520982657. doi: 10.1177/0300060520982657. PMID: 33472489; PMCID: PMC7829611.
- Song Y, Sun Z, Guo C et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subspecies bulgaricus isolated from naturally fermented dairy foods. Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 4;6:22704. doi: 10.1038/srep22704. PMID: 26940047; PMCID: PMC4778129.
- Santos Rocha C, Gomes-Santos AC, Garcias Moreira T et al. Local and systemic immune mechanisms underlying the anti-colitis effects of the dairy bacterium Lactobacillus delbrueckii. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e85923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085923. PMID: 24465791; PMCID: PMC3897545.
- Grigoroff S. Etude Sur Le Lait Fermenté Comestible: Le “KisséLo-MléKo” de Bulgarie. Rev MeDicale Suisse Romande. 1905.
- Drossman DA, Hasler WL. Rome IV-Functional GI Disorders: Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology. 2016 May;150(6):1257-61. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.035. PMID: 27147121.
- Kok CR, Hutkins R. Yogurt and other fermented foods as sources of health-promoting bacteria. Nutr Rev. 2018 Dec 1;76(Suppl 1):4-15. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy056. PMID: 30452699.
- Литинская Е.В. Опыт лечебного применения гастрофарма у больных язвенной болезнью. Врачебное дело. 1982. № 1. С. 70-73.
- Fatani A, Vaher K, Rivero-Mendoza D, Alabasi K, Dahl WJ. Fermented soy supplementation improves indicators of quality of life: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial in adults experiencing heartburn. BMC Res Notes. 2020 Aug 3;13(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-05205-z. PMID: 32746904; PMCID: PMC7397630.
- Lee M, Kim D, Kim H, Jo S, Kim OK, Lee J. Gastro-Protective Effect of Fermented Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) in a Rat Model of Ethanol/HCl-Induced Gastric Injury. Nutrients. 2022 May 16;14(10):2079. doi: 10.3390/nu14102079. PMID: 35631223; PMCID: PMC9147855.
- Olorocisimo JP, Diaz LA, Co DE, Carag HM, Ibana JA, Velarde MC. Lactobacillus delbrueckii reduces anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish through a gut microbiome — brain crosstalk. Neuropharmacology. 2023 Mar 1;225:109401. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109401. Epub 2022 Dec 21. PMID: 36565853.
- Zhang J, Wu HM, Wang X et al. Efficacy of prebiotics and probiotics for functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Feb;99(7):e19107. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019107. PMID: 32049821; PMCID: PMC7035106.
- Wallace C, Gordon M, Sinopoulou V, Akobeng AK. Probiotics for management of functional abdominal pain disorders in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 17;2(2):CD012849. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012849.pub2. PMID: 36799531; PMCID: PMC9945052.