Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Ретроспективне дослідження частоти діагностування дифузних змін паренхіми печінки за результатами радіологічних досліджень
Авторы: Зюзь Н.Ю., Богомаз В.М.
Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
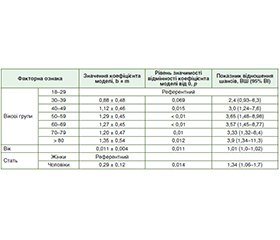
Актуальність. Поширеність хронічної патології печінки є значною і зростає в більшості країн світу. Мета: проаналізувати частоту діагностування структурних дифузних змін печінки радіологічними методами в різних статево-вікових групах дорослого населення. Матеріали та методи. Досліджено 65 570 унікальних протоколів ультразвукових досліджень та 1212 МРТ-досліджень гепатобіліарної системи пацієнтів віком 18 років і старше. При статистичному аналізі кількісних ознак проводилася перевірка розподілу показників на нормальність за критерієм Шапіро — Уїлка. Для проведення порівняння частот використаний критерій хі-квадрат. Для з’ясування зв’язку ризику виникнення дифузних змін печінки з факторними ознаками використано метод побудови моделей логістичної регресії. Для оцінки ступеня вираженості зв’язку між ознаками розраховано показник відношення шансів (ВШ) та його 95% вірогідний інтервал (ВІ). Для оцінки якості прогнозу моделі розраховано аrea under the curve (AUC) та її 95% ВІ. Рівень статистичної значущості вибраний на рівні 5 % (р = 0,05). Дослідження ухвалено локальною етичною комісією. Результати. Частота діагностування дифузних змін паренхіми печінки при ультразвуковому дослідженні у В-режимі в загальній вибірці становила 12,5 % (у жінок — 8,7 %, у чоловіків — 18,2 %). Знайдено статистично значиме збільшення (р < 0,01) шансу розвитку дифузних змін печінки за даними УЗД (ВШ = 1,01, 95% ВІ 1,01–1,02) зі збільшенням віку на кожен рік. В однофакторній моделі логістичної регресії чоловіки, за даними УЗД, мали в 2,3 раза вищі шанси розвитку дифузних змін печінки, ніж жінки (р < 0,01), AUC = 0,604 (95% ВI 0,598–0,61). У загальній вибірці пацієнтів, яким виконано МРТ гепатобіліарної системи, частота діагностування жирової інфільтрації печінки становила 37 % (95% ВІ 34,3–39,8 %). Зокрема, серед 700 жінок частота інцидентів була 34,1 % (95% ВІ 30,7–37,7 %), серед 512 чоловіків — 41,0 % (95% ВІ 36,8–45,3 %). Висновки. Частота діагностування дифузних змін печінки є достатньо високою (12,5 % за даними УЗД та 37 % за даними МРТ) і зростає з віком серед дорослого працездатного населення. З огляду на різноманіття чинників прогресування хронічних захворювань печінки та важливість виокремлення пацієнтів високого ризику розвитку цирозу печінки, потрібне широке впровадження неінвазивних діагностичних тестів, технічне дооснащення спеціалізованих закладів охорони здоров’я. Отримані дані можуть бути орієнтирами для розрахунку потреб у вторинній медичній допомозі та вдосконалення клінічних маршрутів пацієнтів.
Background. The prevalence of chronic liver pathology is high and increasing in most countries of the world. Objective: to evaluate the incidence rate of structural diffuse changes in the liver using radiological methods in different sex-age groups of the adult population. Materials and methods. 65,570 unique protocols of ultrasound examination and 1,212 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hepatobiliary system were studied in patients aged 18 years and older. During the statistical analysis of quantitative features, the distribution of indicators for normality was checked according to the Shapiro-Wilk test. The chi-square test was used to compare frequencies. To determine the relationship between the risk of diffuse liver changes and factor characteristics, we used the method of building logistic regression models. To assess the relationship between the factor traits and the resulting trait, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated. To assess the quality of the model’s prediction, the area under the curve (AUC) and 95% CI were calculated. The level of statistical significance was chosen at 5 % (p = 0.05). The study was approved by the local ethics committee. Results. The frequency of diagnosing diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma during B-mode ultrasound examination in the total sample was 12.5 % (in women — 8.7 %, in men — 18.2 %). A statistically significant increase (p < 0.01) in the risk of developing diffuse changes in the liver was found (OR = 1.01 (95% CI 1.01–1.02 %) with increasing age for each year. In the univariate logistic regression model, men had a 2.3 times higher chances of developing diffuse liver changes than women (p < 0.01), AUC = 0.604 (95% CI 0.598–0.61 %). In the general sample of patients who underwent MRI of the hepatobiliary system, the frequency of diagnosing fatty infiltration of the liver was 37 % (95% CI 34.3–39.8 %). In particular, among 700 women, the frequency of incidents was 34.1 % (95% CI 30.7–37.7 %), among 512 men — 41.0 % (95% CI 36.8–45.3 %). Conclusions. The prevalence of diffuse liver changes is high (12.5 % according to ultrasound and 37 % according to MRI) and increases with age among the adult population of working age. Given the variety of factors contributing to the progression of chronic liver diseases and the importance of identifying patients at high risk of developing liver cirrhosis, there is a need for widespread implementation of non-invasive diagnostic tests and technical upgrading of specialized healthcare facilities. The data obtained can serve as landmarks for calculating the needs for secondary care and improving clinical pathways for patients.
хронічні захворювання печінки; ультразвукова діагностика; МРТ
chronic liver diseases; ultrasound diagnosis; magnetic resonance imaging
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Bogomaz V, Natrus L, Ziuz N and Starodub T. Management of gallstone disease and chronic liver diseases during the COVID-19 outbreak in Ukraine: an ecological study, International Journal of Health Governance. 2023;29(1):45-53. doi: 10.1108/IJHG-09-2023-0087.
- Ciećko-Michalska I, Szczepanek M, Tobiasz-Adamczyk B, Mach T. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Poland: how and at what stage is diagnosed, and how is treated. A survey study. Prz Gastroenterol. 2019;14(3):173-177. doi: 10.5114/pg.2019.88165.
- Danielsson O, Vesterinen T, Arola J, Åberg F, Nissinen MJ. Coexistence of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and autoimmune or toxic liver disease. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology. July 2024;36(7):961-969. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002785.
- Dasarathy S, Dasarathy J, Khiyami A, Joseph R, Lopez R, McCullough AJ. Validity of real time ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis: a prospective study. J Hepatol. 2009;51:1061-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.09.001.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Clinical Practice Guideline Panel, Chair: EASL Governing Board representative, & Panel members (2021). EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis — 2021 update. Journal of Hepatology. 2021;75(3):659-689. doi: 10.1016/–j.jhep.2021.05.025.
- Ferraioli G, Soares Monteiro LB. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:6053-6062. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6053.
- Gu J, Liu S, Du S, et al. Diagnostic value of MRI-PDFF for hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-–analysis. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:3564-3573. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06072-4.
- Hepburn MJ, Vos JA, Fillman EP, Lawitz EJ. The accuracy of the report of hepatic steatosis on ultrasonography in patients infected with hepatitis C in a clinical setting: a retrospective observational study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2009;5:14. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-5-14.
- Hernaez R, Lazo M, Bonekamp S, Kamel I, Brancati FL, Guallar E, Clark JM. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of ultrasonography for the detection of fatty liver: a meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011;54:1082-1090. doi: 10.1002/hep.24452.
- Huang, DQ, Fowler KJ, Liau J, et al. Comparative efficacy of an optimal exam between ultrasound versus abbreviated MRI for HCC screening in NAFLD cirrhosis: A prospective study. Alimentary Рharmacology & Тherapeutics. 2022;55(7):820-827. doi: 10.1111/apt.16844.
- Ichikawa S, Goshima S. Clinical Significance of Liver MR Imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2023 Apr 1;22(2):157-175. doi: 10.2463/mrms.rev.2022-0100.
- Kudo M, Zheng RQ, Kim SR, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ima–ging for liver cirrhosis compared to histologically proven liver cirrhosis. A multicenter collaborative study. Intervirology. 2008;51(1):17-26. doi: 10.1159/000122595.
- Luca M, Ignazio G, Francesco L, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of fibrosis in Italian primary care services: GPS-NAFLD Study. Liver international: official journal of the International Association for the Study of Disease. 2022;42(12):2632-2645. doi: 10.1111/liv.15443.
- Moon AM, Singal AG, Tapper EB. Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;18(12):2650-2666. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.060.
- Ronot M, Leporq B, Van Beers BE, Vilgrain V. CT and MR perfusion techniques to assess diffuse liver disease. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020;45:3496-3506. doi: 10.1007/s00261-019-02338-z.
- Vernuccio F, Cannella R, Bartolotta TV, et al. Advances in liver US, CT, and MRI: moving toward the future. 2021;5:52. doi: 10.1186/s41747-021-00250-0.
- Younossi ZM, Wong G, Anstee QM, & Henry L. The Global Burden of Liver Disease. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2023;21(8):1978-1991. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.015.
- Ziuz N, Bogomaz V. Ultrasound technologies in algorithms for the management of chronic liver diseases. Clinical and Preventive Medicine. 2024;4:94-102. doi: 10.31612/2616-4868.4.2024.13.