Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Хронічний абдомінальний біль. Робота на стику гастроентерології та психіатрії
Авторы: Губська О.Ю.
Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
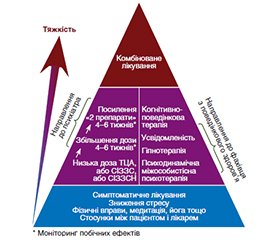
Актуальність. Синдром хронічного абдомінального болю є одним із проявів розладів кишково-мозкової взаємодії (РКМВ), що посідають значне місце серед гастроінтестинальних патологій, але залишаються недостатньо розпізнаваними у клінічній практиці. Як конкретний прояв цього розладу у сучасній літературі виокремлюється центрально-опосередкований біль у животі (ЦОБЖ) або ж центрально-опосередкований больовий синдром (ЦОБС). Це захворювання охоплює низку шлунково-кишкових та позашлунково-кишкових симптомів та є тісно асоційованим із психологічним дистресом, неврологічними та психічними розладами. З огляду на зростання стресових чинників у сучасному світі та постійний дистрес воєнного часу в Україні, діагностика ЦОБЖ потребує від лікарів-клініцистів розуміння взаємозв’язку центральної нервової системи та гастроінтестинальних захворювань на кожній ланці системи охорони здоров’я. Мета: виконати огляд публікацій, що висвітлюють патогенез, загальні принципи діагностики та лікування ЦОБЖ як самостійної нозології у категорії розладів по осі кишечник — головний мозок, а також звернути увагу на потребу у комплексному психосоматичному підході до ведення пацієнтів із цим захворюванням. Матеріали та методи. Виконано пошук статей, присвячених функціональним гастроінтестинальним розладам та хронічному абдомінальному болю, у вітчизняних та закордонних виданнях. Використано 25 публікацій за період з 1982 по 2024 р. Серед них 8 % були опубліковані в Україні, а 92 % — за кордоном. Публікації були присвячені наступним темам: хронічний абдомінальний біль як такий — 13 статей, діагностика функціональних розладів у контексті хірургії — 3 статті, психосоматичний вплив на гастроінтестинальні патології — 3 статті, нейромодуляторна фармакотерапія — 2 статті, комунікація та психотерапевтичні стратегії у веденні пацієнтів із РКМВ — 4 статті. Обговорення. Розвиток ЦОБЖ зумовлений центральною сенситизацією. Через потребу в виключенні органічної патології та тривалому спостереженні за пацієнтом, а також через асоціацію діагнозу із психічними патологіями критичним фактором у його встановленні є ретельно зібраний анамнез, зосереджений на описі болю. Основою фармакологічної терапії ЦОБЖ є антидепресанти, серед яких провідну роль відіграють трициклічні антидепресанти через їх виражений аналгетичний ефект у низьких дозах, але важливе місце займають також інгібітори зворотного захоплення серотоніну/норадреналіну) як препарати вибору у хворих із хронічним болем та депресивними станами. Ефективність медикаментозного лікування посилюється в комплексній терапії та поєднанні із методами психотерапевтичного втручання, які мають пропонуватися пацієнтам якомога раніше. Висновки. ЦОБЖ як представник групи РКМВ є шлунково-кишковим больовим розладом із центральною детермінантою. Через зростаючу клінічну поширеність та складність цієї групи захворювань існує нагальна потреба у комплексному підході до їх ведення, що виходить із сучасної біопсихосоціальної моделі. Вибір терапії має враховувати усі особливості виникнення та перебігу захворювання, а обрані психофармакологічні засоби та психотерапевтичні втручання мають бути обґрунтованими і ефективними.
Background. Chronic abdominal pain syndrome is one of the manifestations of gut-brain interaction disorders, which occupy a significant place among gastrointestinal pathologies, but remain insufficiently recognized in clinical practice. Centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome (CAPS) is singled out as a specific manifestation of this disorder in modern literature. This disease encompasses a range of gastrointestinal and extra-gastrointestinal symptoms and is closely associated with psychological distress, neurological and psychiatric disorders. Given an increase in stress factors in the modern world and the constant distress of wartime in Ukraine, the diagnosis of CAPS requires from clinicians an understanding of the relationship between the central nervous system and gastrointestinal diseases at each link of the health care system. Purpose: to review publications on the pathogenesis, general principles of diagnosis and treatment of CAPS as an independent nosology in the category of the gut-brain axis disorders (GBAD), as well as to draw attention to the need for a comprehensive psychosomatic approach to the management of patients with this disease. Materials and methods. A search was made for articles covering functional gastrointestinal disorders and chronic abdominal pain in domestic and foreign publications. Twenty-five works were used for the period from 1982 to 2024. Among them, 8 % were published in Ukraine, and 92 % — abroad. The publications considered the following topics: chronic abdominal pain as such — 13 articles, diagnosis of functional disorders in the context of surgery — 3 articles, psychosomatic influence on gastrointestinal pathologies — 3 articles, neuromodulation pharmacotherapy — 2 articles, communication and psychotherapeutic strategies in the management of patients with GBAD — 4 articles. Discussion. The development of CAPS is caused by central sensitization. Due to the need to exclude organic pathology and in a long-term observation of the patient, as well as due to the association of the diagnosis with mental pathologies, a critical factor is a thorough history collection, focusing on the description of pain. Antidepressants are the basis of pharmacological therapy for CAPS, with tricyclic antidepressants play a leading role due to their pronounced analgesic effect in low doses, but selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are also important as the drugs of choice in patients with chronic pain and depressive states. The effectiveness of drug treatment is enhanced in comprehensive therapy and combination with psychotherapeutic intervention methods, which should be offered to patients as early as possible. Conclusions. CAPS as a representative of the GBAD group is a gastrointestinal pain disorder with a central determinant. Due to the growing clinical prevalence and complexity of this group of diseases, there is an urgent need for a comprehensive approach to their management based on the modern biopsychosocial model. The choice of therapy should include all the features of the occurrence and course of the disease, and psychopharmacological agents and psychotherapeutic interventions chosen should be justified and effective.
розлади осі кишечник — мозок; хронічний абдомінальний біль; центрально-опосередкований біль у животі; центрально-опосередкований больовий синдром; психосоматичні розлади; функціональні розлади травлення
gut-brain axis disorders; chronic abdominal pain; centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome; psychosomatic disorders; functional gastrointestinal disorders
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Treede RD, Rief W, Barke A, et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: the IASP classification of chronic pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain. 2019 Jan;160(1): 19-27.
- Sjölund J, Uusijärvi A, Tornkvist NT, et al. Prevalence and Progression of Recurrent Abdominal Pain, From Early Childhood to Adolescence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(5):930-938.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.047.
- Yarger E, Sandberg K. Updates in diagnosis and management of chronic abdominal pain. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2020 Aug;50(8):100840.
- Sabo CM, Grad S, Dumitrascu DL. Chronic abdominal pain in general practice. Dig Dis. 2021;39(6):606-14.
- Assessment of chronic abdominal pain. Available from: https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/767. Accessed: September 02, 2024.
- Губська О.Ю., Прикащикова Г.І. Психогастроентерологія розладів кишково-мозкової взаємодії. Огляд літератури з власними дослідженнями. Сучасна гастроентерологія. 2023;131(3). doi: 10.30978/MG-2023-3-61. Посилання: http://sgastro.com.ua/article/view/283275.
- Korterink J, Devanarayana NM, Rajindrajith S, et al. Childhood functional abdominal pain: mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;12(3):159-71.
- Wallander MA, Johansson S, Ruigomez A, et al. Unspecified abdominal pain in primary care: the role of gastrointestinal morbidity. Int J Clin Pract. 2007 Oct;61(10):1663-70.
- Viniol A, Keunecke C, Biroga T, et al. Studies of the symptom abdominal pain — a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fam Pract. 2014 Oct;31(5):517-29.
- Freeman TR, Stewart M, Léger D, et al. Natural history of abdominal pain in family practice: longitudinal study of electronic medical record data in southwestern Ontario. Can Fam Physician. 2023 May;69(5):341-51.
- Price SJ, Gibson N, Hamilton WT, et al. Diagnoses after newly recorded abdominal pain in primary care: observational cohort study. Br J Gen Pract. 2022 Aug;72(721):e564-70.
- Keefer L, Drossman DA, Guthrie E, et al. Centrally mediated disorders of gastrointestinal pain. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:1408-1419. Available from: https://theromefoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/centrally-mediated-disorders-of-gastrointestinal-pain.pdf.
- Longstreth GF, Yao JF. Irritable bowel syndrome and surgery: a multivariable analysis. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1665-1673.
- Reimerink JJ, van der Laan MJ, Koelemay MJ, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of population based mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2013;100:1405-1413.
- Drossman DA. Diagnosing and treating patients with refractory functional gastrointestinal disorders. Ann Intern Med. 1995;123:688-697.
- Drossman DA. Patients with psychogenic abdominal pain: six years’ observation in the medical setting. Am J Psychiatry. 1982;139:1549-1557.
- Leserman J, Drossman DA, Li Z, et al. Sexual and physical abuse history in gastroenterology practice: how types of abuse impact health status. May 2016 Centrally Mediated Disorders of GI Pain 1417 CNS-PAIN. Psychosom Med. 1996;58:4-15.
- Drossman DA, Leserman J, Hu JB. Gastrointestinal diagnosis, abuse history, and effects on health status. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:1159-1161.
- Sperber AD, Morris CB, Greemberg L, et al. Development of abdominal pain and IBS following gynecological surgery: a prospective, controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:75-84.
- Drossman DA. 2012 David Sun Lecture: helping your patient by helping yourself: How to improve the patient-physician relationship by optimizing communication skills. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013:521-528.
- Drossman DA. Presidential address: gastrointestinal illness and biopsychosocial model. Psychosom Med. 1998;60:258-267.
- Halpert A, Dalton CB, Diamant NE, et al. Clinical response to tricyclic antidepressants in functional bowel disorders is not related to dosage. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:664-671.
- Gaynor PJ, Gopal M, Zheng W, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of major depressive disorder and associated painful physical symptoms: a replication study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27:1859-1867.
- Губська О.Ю., Алексєєва В.В., Дудко О.В., Кузьмінець А.А., Божицька О.М., Мафтичук Б.Р. Систематичний огляд досліджень з ефективності біосугестивної терапії в корекції психосоматичних порушень: фокус на розлади кишково-мозкової взаємодії. Гастроентерологія. 2023;57(4):75-84. Посилання: http://www.mif-ua.com/media/uploads/arhiv/gastro/2023/4(tom%2057)/MVZ_Gastro-4_(tom57)(zak90)_2023.pdf; https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/symptoms-of-gastrointestinal-disorders/chronic-abdominal-pain-and-recurrent-abdominal-pain#Evaluation_v887591.