Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Новітні діагностичні методи досліджень стравоходу та шлунка. Високороздільна манометрія уже в Україні
Авторы: Степанов Ю.М., Пролом Н.В., Тарабаров С.О.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
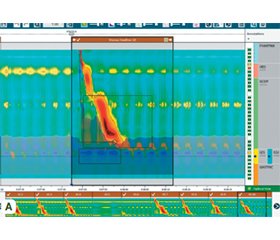
На сьогодні існує кілька передових методів діагностики патології стравоходу та шлунка, які активно застосовуються в клінічній практиці, серед них особливо виділяється високороздільна манометрія (HR-манометрія). Це інноваційне дослідження надає можливість детально оцінити функціональний стан стравоходу, зокрема координацію скорочень м’язів під час ковтання та роботу нижнього стравохідного сфінктера (НСС). HR-манометрія є ефективним інструментом для виявлення порушень моторики, як-от ахалазія стравоходу, гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба (ГЕРХ), дифузний спазм стравоходу, а також інших функціональних розладів, що можуть впливати на процес ковтання та переміщення їжі по стравоходу. Однією з основних переваг HR-манометрії є її здатність точно діагностувати функціональні розлади стравоходу завдяки використанню спеціальних катетерів із численними датчиками, що розташовані на невеликій відстані один від одного (близько 1 см). Це дозволяє створювати детальні топографічні карти тиску в стравоході, які в реальному часі відображають скорочення його м’язів. Завдяки такій високій роздільній здатності можна виявляти навіть найдрібніші порушення моторики, що раніше залишалися непоміченими при традиційних методах діагностики. HR-манометрія значно поліпшила діагностику ахалазії стравоходу завдяки можливості чітко визначати три підтипи цього захворювання (класична ахалазія, панезофагеальний тиск і спастична ахалазія). Це дозволяє лікарям не тільки точніше встановлювати діагноз, але й обирати оптимальну стратегію лікування, адаптовану до конкретного типу порушення. У випадку ГЕРХ HR-манометрія допомагає оцінити функцію НСС та діафрагми, що важливо для виявлення слабкості діафрагмального бар’єра, який є однією з основних причин патологічного рефлюксу. Крім того, цей метод дозволяє діагностувати супутні порушення перистальтики, що впливають на здатність стравоходу очищатися від кислотного рефлюксату, тим самим допомагаючи лікарям краще розуміти механізм виникнення захворювання та призначати більш ефективне лікування. Таким чином, HR-манометрія посідає ключове місце серед сучасних методів діагностики патології стравоходу, дозволяючи не тільки точно виявляти моторні порушення, але й оптимізувати лікування. Це суттєво підвищує якість життя пацієнтів, оскільки допомагає лікарям вибирати найбільш ефективні терапевтичні стратегії, засновані на точних даних про функцію стравоходу.
To date, there are several advanced methods for diagnosing esophageal and gastric disorders that are actively used in clinical practice, among which high-resolution (HR) manometry stands out. This innovative study provides an opportunity to assess in detail the functional state of the esophagus, in particular the coordination of muscle contractions during swallowing and the function of the lower esophageal sphincter. HR manometry is an effective tool for detecting motility disorders such as achalasia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, diffuse esophageal spasm, as well as other functional disorders that can affect the process of swallowing and moving food through the esophagus. One of the main advantages of HR manometry is accurate diagnosis of functional esophageal disorders due to the use of special catheters with numerous sensors located at a short distance from each other (about 1 cm). This allows you to create detailed topographic maps of pressure in the esophagus, which show the contraction of its muscles in real time. Thanks to this high resolution, it is possible to detect even minor motility disorders that previously went unnoticed when using traditional diagnostic methods. HR manometry has significantly improved the diagnosis of achalasia due to the ability to clearly identify three subtypes of this disease (classic achalasia, pan-esophageal pressure, and spastic achalasia). This allows doctors not only to make a more accurate diagnosis, but also to choose the optimal treatment strategy adapted to the specific type of disorder. In case of gastroesophageal reflux disease, HR manometry helps assess the function of the lower esophageal sphincter and diaphragm, which is important for detecting diaphragmatic weakness, which is one of the main causes of pathological reflux. In addition, this method makes it possible to diagnose concomitant peristalsis disorders that affect the ability of the esophagus to clear from acid reflux, thereby helping doctors better understand the mechanism of the disease and prescribe more effective treatment. Thus, HR manometry has a key place among modern methods for diagnosing esophageal disorders, allowing not only to accurately detect motility disorders, but also to optimize treatment. This significantly improves patients’ quality of life, as it helps doctors choose the most effective therapeutic strategies based on accurate data about esophageal function.
високороздільна манометрія (HR-манометрія); захворювання шлунково-кишкового тракту
high-resolution manometry; gastrointestinal diseases
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Pandolfino JE, Kwiatek MA, Nealis T, Bulsiewicz W, Post J, Kahrilas PJ. Achalasia: a new clinically relevant classification by high-resolution manometry. Gastroenterology. 2008. № 135(5). P. 1526-33. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.022.
- International High Resolution Manometry Working Group. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0 / PJ Kahrilas et al. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. № 27(2). P. 160-74. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12477.
- Krause AJ, Carlson DA. Dysphagia: Novel and Emerging Diag–nostic Modalities. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2021. № 50(4). P. 769-790. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2021.07.003.
- Modern diagnosis of GERD: the Lyon / CP Gyawali et al. Consensus. Gut. 2018. № 67(7) P. 1351-1362. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722.
- Pandolfino JE, Gawron AJ. High-resolution manometry: indications and clinical applications. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013. № 42(1). P. 27-37.
- The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v4.0. / PJ Kahrilas et al. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. № 33(1). doi: 10.1111/nmo.14058.
- Duy L, Clayton S, Morimoto N, Wang S, DiSantis D. Beyond visualizing the bird beak: esophagram, timed barium esophagram and manometry in achalasia and its 3 subtypes. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04554-8. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39317828.
- Clinical characteristics of absent contractility and ineffective esophageal motility: a multicenter study in Japan / Y Ikebuchi et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. № 38(11). Р. 1926-1933. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16268.
- Savarino E, Bhatia S, Roman S, Sifrim D, Tack J, Thompson SK, Gyawali CP. Achalasia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022. № 8(1). Р. 28. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00356-8.
- Rohof WOA, Bredenoord AJ. Chicago Classification of Eso–phageal Motility Disorders: Lessons Learned. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017. № 19(8). Р. 37. doi: 10.1007/s11894-017-0576-7.
- Low EXS, Wang YP, Ye YC, Liu PY, Sung KY, Lin HE, Lu CL. A Comparison between Chicago Classification Versions 3.0 and 4.0 and Their Impact on Manometric Diagnoses in Esophageal High-Resolution Manometry Cases. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. № 14(3) Р. 263. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030263.
- Jung KW. [Chicago Classification ver. 4.0: Diagnosis of Achalasia and Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022. № 79(2). Р. 61-65. Korean. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.017.
- Horton A, Jawitz N, Patel A. The Clinical Utility of Provo–cative Maneuvers at Esophageal High-resolution Manometry (HRM). J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021. № 55(2). Р. 95-102. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001466.
- Lee TH. [Chicago Classification ver. 4.0: An Overview of Esophageal Motility Disorders on High-resolution Manometry]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022. № 79(2). Р. 55-60. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.015.
- Fox MR, Sweis R, Yadlapati R, Pandolfino J, Hani A, Defilippi C, Jan T, Rommel N. Chicago classification version 4.0© technical review: Update on standard high-resolution manometry protocol for the assessment of esophageal motility. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. № 33(4). e14120. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14120.
- Sallette M, Lenz J, Mion F, Roman S. From Chicago classification v3.0 to v4.0: Diagnostic changes and clinical implications. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023. № 35(1). e14467. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14467.
- Novel scale for evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of per-oral endoscopic myotomy in achalasia / K Takahashi et al. J Gastroenterol. 2024. № 59(8). Р. 658-667. doi: 10.1007/s00535-024-02119-6.
- Yodice M., Mignucci A., Shah V., Ashley C., Tadros M. Preoperative physiological esophageal assessment for anti-reflux surgery: a guide for surgeons on high-resolution manometry and pH testing. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. № 27. P. 1751-1769. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1751.
- Riva CG, Siboni S, Sozzi M, Lazzari V, Asti E, Bonavina L. High-resolution manometry findings after Linx procedure for gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020. № 32(3). e13750. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13750.
- Stadnicki A, Kurek J, Klimacka-Nawrot E, Stadnicka A, Rerych K. Identification of Sliding Hiatus Hernia by High-Resolution Manometry and Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy in Patients with Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022. № 11. P. 6906. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11236906.
- Utilizing Esophageal Motility Tests in Diagnosing and Evaluating Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease / W. Yang et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. № 14(14). Р. 1467. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14141467.
- Garbarino S, Horton A, Patel A. The Utility of Esophageal Motility Testing in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019. № 21(8). Р. 37. doi: 10.1007/s11894-019-0704-7.
- Layne SJ, Lorsch ZS, Patel A. Novel Diagnostic Techniques in the Evaluation of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Dig Dis Sci. 2023. № 68(6). Р. 2226-2236. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-07901-9.
- Ineffective esophageal motility in Chicago Classification version 4.0 better predicts abnormal acid exposure / QJ et al. Zhuang Esophagus. 2022. № 19(1). Р. 197-203. doi: 10.1007/s10388-021-00867-5.
- de Padua F, Herbella FAM, Patti MG. The prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in named manometric patterns of dysmotility according to the Chicago Classification 4.0. Dis Esophagus. 2022. № 35(10). doac023. doi: 10.1093/dote/doac023.
- High-resolution manometry is superior to endoscopy and radiology in assessing and grading sliding hiatal hernia: A comparison with surgical in vivo evaluation / S Tolone et al. United European Gastroenterology Journal. 2018. № 6(7). Р. 981-989. https://doi.org/–10.1177/2050640618769160.
- High-resolution 3-dimensional tomography may be a useful tool for understanding the anatomy of hiatal hernias and surgical planning of patients eligible for laparoscopic or robotic antireflux surgery / A.V. Santana et al. Surg Endosc. 2023. Vol. 38. P. 780-786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10599-5.
- Esophagogastric junction morphology assessment by high resolution manometry in obese patients candidate to bariatric surgery / S Tolone et al. Int J Surg. 2016. № 28(1). Р. 109-13. doi: 10.1016/–j.ijsu.2015.12.047.
- Rengarajan A, Gyawali CP. High-resolution Manometry can Characterize Esophagogastric Junction Morphology and Predict Esophageal Reflux Burden. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2020. № 54(1). Р. 22-27. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001205.
- Fox M, Bredenoord AJ. High-resolution manometry: moving from research into clinical practice. Gut. 2008. № 57(3). Р. 405-423. doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.126128.
- Preoperative diagnostic workup before antireflux surgery: an evidence and experience-based consensus of the Esophageal Diagnostic Advisory Panel / BA Jobe et al. J Am Coll Surg. 2013. № 217(4). Р. 586-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.05.023.