Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 21, №2, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Блокада квадратного м’яза попереку як компонент знеболювання при лапароскопічній холецистектомії
Авторы: Чуклін С.М., Чуклін С.С.
Медичний центр Святої Параскеви, м. Львів, Україна
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
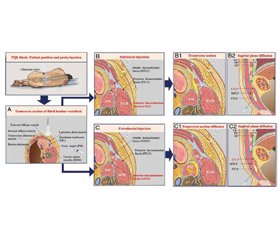
Лапароскопічна холецистектомія є малоінвазивною процедурою. Проте вона може викликати сильний післяопераційний біль, а іноді і хронічний. Цей біль виникає внаслідок кількох причин: введення троакарів, загоєння ран, маніпуляції з жовчним міхуром і оточуючими органами, запалення, відображений біль у плечі, інсуфляція вуглекислого газу, випадкове пошкодження нерва. Для лікування післяопераційного болю часто використовується комбінація методів, включно зі знеболювальними (нестероїдні протизапальні засоби та опіоїди), регіонарною анестезією, належним доглядом за ранами. Блокада квадратного м’яза попереку (QLB) — це техніка регіонарної анестезії, яка може використовуватися при лапароскопічній холецистектомії для забезпечення післяопераційної аналгезії. Вона передбачає введення місцевого анестетика в QL, який розташований збоку від нижньої частини спини. Ін’єкція місцевого анестетика поблизу квадратного м’яза попереку може блокувати грудопоперекові нерви та забезпечити знеболювання верхньої та нижньої частини живота. Блокади QL зазвичай забезпечують сенсорне блокування таких дерматомів: Т12, L1, L2, L3. На ступінь дерматомного покриття можуть впливати такі чинники, як об’єм використаного місцевого анестетика, конкретне місце ін’єкції та індивідуальні анатомічні варіації. QLB забезпечує ефективне лікування болю після абдомінальної операції; допомагає зменшити потребу в опіоїдах, які можуть мати побічні ефекти; поліпшує одужання пацієнта. Потрібні подальші дослідження, щоб вивчити довгострокові переваги та оптимальні методи QLB у цій ситуації.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive procedure. However, it can cause severe postoperative pain, and sometimes chronic pain. This pain results from several causes: trocar insertion, wound healing, surgical manipulation with the gallbladder and surrounding organs, inflammation, referred shoulder pain, carbon dioxide insufflation, accidental nerve damage. A combination of methods is often used to treat postoperative pain, including analgesics (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioids), regional anesthesia, and proper wound care. The quadratus lumborum (QL) block is a regional anesthetic technique that can be used in laparoscopic cholecystectomy to provide postoperative analgesia. It involves injecting a local anesthetic agent into the QL muscle, which is located on the side of the lower back. Injection of a local anesthetic near the quadratus lumborum muscle can block the thoracolumbar nerves and provide pain relief in the upper and lower abdomen. QL blocks generally provide sensory block to the following dermatomes: T12, L1, L2, L3. The degree of dermatomal coverage can be influenced by factors such as the volume of local anesthetic used, the specific injection site, and individual anatomical variations. QL block provides effective pain management after abdominal surgery; helps reduce the need for opioids, which can have side effects; improves the patient’s recovery. Further research is needed to explore the long-term benefits and optimal techniques for QL block in this setting.
лапароскопічна холецистектомія; біль; знеболювання; регіонарна анестезія; блокада квадратного м’яза попереку
laparoscopic cholecystectomy; pain; analgesia; regional anesthesia; quadratus lumborum block
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Kumar M, Yadav JBS, Singh AK, Kumar A, Singh D. Comparative Study Between Conventional Landmark Versus Ultrasound-Guided Paravertebral Block in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Controlled Study. Cureus. 2023;15(3):e36768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36768.
- Aydin G, Aydin O. The Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Paravertebral Block in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Medicina (Kaunas). 2018;54(5):75. doi: 10.3390/medicina54050075.
- Grape S, Kirkham KR, Akiki L, Albrecht E. Transversus abdominis plane block versus local anesthetic wound infiltration for optimal analgesia after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. J Clin Anesth. 2021;75:110450. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2021.110450.
- Uyar S, Tire Y, Kozanhan B. The effect of upper transabdominal plane block on diaphragm thickness in adult patients after laparoscopic cholecystectomy operation. J Minim Access Surg. 2024 Mar 28. doi: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_401_23. Online ahead of print.
- Bourgeois C, Oyaert L, Van de Velde M, Pogatzki-Zahn E, Freys SM, Sauter AR, et al. Pain management after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review and procedure-specific postoperative pain management (PROSPECT) recommendations. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2024 Aug 12. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000002047. Online ahead of print.
- Kummer I, Lüthi A, Klingler G, Andereggen L, Urman RD, Luedi MM, et al. Adjuvant Analgesics in Acute Pain - Evaluation of Efficacy. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024;28(9):843-852. doi: 10.1007/s11916-024-01276-w.
- Levy N, Quinlan J, El-Boghdadly K, Fawcett WJ, Agarwal V, Bastable RB, et al. An international multidisciplinary consensus statement on the prevention of opioid-related harm in adult surgical patients. Anaesthesia. 2021;76(4):520-536. doi: 10.1111/anae.15262.
- Macintyre PE, Quinlan J, Levy N, Lobo DN. Current Issues in the Use of Opioids for the Management of Postoperative Pain: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2022;157(2):158-166. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.6210.
- Barazanchi AWH, MacFater WS, Rahiri JL, Tutone S, Hill AG, Joshi GP; PROSPECT collaboration. Evidence-based management of pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a PROSPECT review update. Br J Anaesth. 2018;121(4):787-803. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.06.023.
- Jiang B, Ye S. Pharmacotherapeutic pain management in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A review. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2022;31(11):1275-1288. doi: 10.17219/acem/151995.
- Houben AM, Moreau AJ, Detry OM, Kaba A, Joris JL. Bilateral subcostal transversus abdominis plane block does not improve the postoperative analgesia provided by multimodal analgesia after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2019;36(10):772-777. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001028.
- Ozciftci S, Sahiner Y, Sahiner IT, Akkaya T. Is Right Unilateral Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP) Block Successful in Postoperative Analgesia in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy? Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:2668215. doi: 10.1155/2022/2668215.
- Mounika V, Sahu L, Mishra K, Mohapatra PS. A Comparative Evaluation of Post-operative Pain Management Using Erector Spinae Plane Block and Oblique Transverse Abdominis Plane Block in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Cureus. 2023;15(3):e35750. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35750.
- Chou R, Gordon DB, de Leon-Casasola OA, Rosenberg JM, Bickler S, Brennan T, et al. Management of Postoperative Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Committee on Regional Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J Pain. 2016;17(2):131-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.12.008.
- Yılmaz ET, Gülmez DD, Apan A, Keles BO, Coşkun M, Döger C, et al. A novel comparison of erector spinae plane block and paravertebral block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024;70(3):e20231457. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20231457.
- Jeong HW, Kim CS, Choi KT, Jeong SM, Kim DH, Lee JH. Preoperative versus Postoperative Rectus Sheath Block for Acute Postoperative Pain Relief after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Rando-mized Controlled Study. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):1018. doi: 10.3390/jcm8071018.
- Jeffrey KN, Thelen AE, Dreimiller AM, Tollinche LE, Alkhatib H, Dorsey A, et al. Laparoscopic transversus abdominis plane block reduces postoperative opioid requirements after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surgery. 2023;173(3):864-869. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2022.07.053.
- Saravanan R, Venkatraman R, Karthika U. Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Modified BRILMA Block with Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block for Postoperative Analgesia in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy — A Randomized Controlled Trial. Local Reg Anesth. 2021;14:109-116. doi: 10.2147/LRA.S316320.
- Bilge A, Başaran B, Altıparmak B, Et T, Korkusuz M, Yarımoğlu R. Comparing ultrasound-guided modified thoracoabdominal nerves block through perichondrial approach with oblique subcostal transversus abdominis plane block for patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized, controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023;23(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02106-z.
- Ahmad F, Ali L, Ahmed M, Yasrab M, Khusdil A, Samiullah. Thoracic Epidural Versus General Anaesthesia For Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2022;34(2):279-282. doi: 10.55519/JAMC-02-9071.
- Liu X, Song T, Chen X, Zhang J, Shan C, Chang L, et al. Quadratus lumborum block versus transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing abdominal surgeries: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020;20(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-00967-2.
- Aygun H, Kavrut Ozturk N, Pamukcu AS, Inal A, Kiziloglu I, Thomas DT, et al. Comparison of ultrasound guided Erector Spinae Plane Block and quadratus lumborum block for postoperative analgesia in laparoscopic cholecystectomy patients; a prospective randomized study. J Clin Anesth. 2020;62:109696. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2019.109696.
- Mansour HS, Ali NS, Rahman MAA. The effect of dexamethasone as an adjuvant in quadratus lumborum block to improves analgesia after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Controlled randomized study. Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia. 2024;40(1):135-142. doi: 10.1080/11101849.2024.2322902.
- Brandão VGA, Silva GN, Perez MV, Lewandrowski KU, Fiorelli RKA. Effect of Quadratus Lumborum Block on Pain and Stress Response after Video Laparoscopic Surgeries: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Pers Med. 2023;13(4):586. doi: 10.3390/jpm13040586.
- Weheba HESM, Abdelsalam T, Ghareeb S, Makharita MY. Posterior Quadratus Lumborum Block versus Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Int J Anesthetic Anesthesiol. 2019;6:093. doi.org/10.23937/2377-4630/1410093.
- Brandão VGА, Silva GN, Alvim Fiorelli RK, Perez MV. Outcome of Ultrasound Guided Anterior Quadratus Lumborum Block After Video Laparoscopic Cholecystectomies: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Surg Innov. 2023;30(3):283-296. doi: 10.1177/15533506231159161.
- Blanco R. Tap block under ultrasound guidance: the description of a “no pops” technique. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007;32(supp.1):130 (A271). doi:10.1136/rapm-00115550-200709001-00249.
- Ueshima H, Otake H, Lin JA. Ultrasound-Guided Quadratus Lumborum Block: An Updated Review of Anatomy and Techniques. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:2752876. doi: 10.1155/2017/2752876.
- Willard FH, Vleeming A, Schuenke MD, Danneels L, Schleip R. The thoracolumbar fascia: anatomy, function and clinical considerations. J Anat. 2012;221(6):507-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01511.x.
- El-Boghdadly K, Elsharkawy H, Short A, Chin KJ. Quadratus Lumborum Block Nomenclature and Anatomical Considerations. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016 Jul-Aug;41(4):548-9. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000411. PMID: 27315184.
- Elsharkawy H. Quadratus lumborum block with paramedian sagittal oblique (subcostal) approach. Anaesthesia. 2016;71(2):241-2. doi: 10.1111/anae.13371.
- Blanco R, Ansari T, Riad W, Shetty N. Quadratus Lumborum Block Versus Transversus Abdominis Plane Block for Postoperative Pain After Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016;41(6):757-762. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000495.
- Wang X, Zhang H, Chen Y, Xie Z, Chen M, Chen Y, et al. The anesthetic efficacy of ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus combined with quadratus lumborum block with Shamrock approach in total hip arthroplasty: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2023;24(1):596. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07619-z.
- Nee R, McDonnell J. Quadratus Lumborum Blocks. https://resources.wfsahq.org/atotw/quadratus-lumborum-blocks.
- Long X, Yin Y, Guo W, Tang L. Ultrasound-guided quadratus lumborum block: a powerful way for reducing postoperative pain. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023;85(10):4947-4953. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001209.
- Elsharkawy H, El-Boghdadly K, Barrington M. Quadratus Lumborum Block: Anatomical Concepts, Mechanisms, and Techniques. Anesthesiology. 2019;130(2):322-335. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002524.
- Akerman M, Pejčić N, Veličković I. A Review of the Quadratus Lumborum Block and ERAS. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:44. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00044.
- Fargaly OS, Boules ML, Hamed MA, Aleem Abbas MA, Shawky MA. Lateral Quadratus Lumborum Block versus Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in Laparoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Study. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2022;2022:9201795. doi: 10.1155/2022/9201795.
- Kelly T, Wolla CD, Wolf BJ, Hay E, Babb S, Wilson SH. Comparison of lateral quadratus lumborum and lumbar plexus blocks for postoperative analgesia following total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2022;47(9):541-546. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2022-103598.
- Fernandes HDS, Azevedo AS, Ferreira TC, Santos SA, Rocha-Filho JA, Vieira JE. Ultrasound-guided peripheral abdominal wall blocks. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021;76:e2170. doi: 10.6061/cli–nics/2021/e2170.
- Lee S, Kang RA, Kim GS, Gwak MS, Choi GS, Kim JM, et al. Comparison of postoperative analgesic effects of posterior quadratus lumborum block and intrathecal morphine in laparoscopic donor hepatectomy: a prospective randomized non-inferiority clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2022;47(9):527-533. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2022-103577.
- Børglum J, Moriggl B, Jensen K, Lønnqvist P-A, Christensen AF, Sauter A, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum Blockade. BJA. 2013;111(Issue eLetters Supplement). doi:10.1093/bja/el_9919.
- Vamnes JS, Sørenstua M, Solbakk KI, Sterud B, Leonardsen AC. Anterior quadratus lumborum block for ambulatory laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled trial. Croat Med J. 2021;62(2):137-145. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2021.62.137.
- Li H, Shi R, Shi D, Wang R, Liu Y, Wang Y. Anterior quadratus lumborum block at the lateral supra-arcuate ligament versus transmuscular quadratus lumborum block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic nephrectomy: A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Anesth. 2021;75:110561. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2021.110561.
- Seidel R, Wree A, Schulze M. Thoracic-paravertebral blocks: comparative anatomical study with different injection techniques and volumes. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2020;45(2):102-106. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100896.
- He WQ, Li YJ, Li YS, Zhang XH, Cao J, Lu KZ, et al. Advantages of Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum Block via Subfascial Approach Versus Extrafascial Approach for Postoperative Analgesia After Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Controlled Study. Clin J Pain. 2022;38(12):730-738. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000001078.
- Adhikary SD, El-Boghdadly K, Nasralah Z, Sarwani N, Nixon AM, Chin KJ. A radiologic and anatomic assessment of injectate spread following transmuscular quadratus lumborum block in cadavers. Anaesthesia. 2017;72(1):73-79. doi: 10.1111/anae.13647.
- Kukreja P, MacBeth L, Sturdivant A, Morgan CJ, Ghanem E, Kalagara H, et al. Anterior quadratus lumborum block analgesia for total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019:rapm-2019-100804. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100804.
- Murouchi T, Iwasaki S, Yamakage M. Quadratus Lumborum Block: Analgesic Effects and Chronological Ropivacaine Concentrations After Laparoscopic Surgery. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016;41(2):146-50. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000349.
- Mitchell KD, Smith CT, Mechling C, Wessel CB, Orebaugh S, Lim G. A review of peripheral nerve blocks for cesarean delivery analgesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019:rapm-2019-100752. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100752.
- Elsharkawy H, El-Boghdadly K, Kolli S, Esa WAS, DeGrande S, Soliman LM, et al. Injectate spread following anterior sub-costal and posterior approaches to the quadratus lumborum block: A comparative cadaveric study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017;34(9):587-595. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000680.
- Nie BQ, Niu LX, Yang E, Yao SL, Yang L. Effect of Subcostal Anterior Quadratus Lumborum Block vs. Oblique Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block after Laparoscopic Radical Gastrectomy. Curr Med Sci. 2021;41(5):974-980. doi: 10.1007/s11596-021-2429-8.
- Chin KJ, McDonnell JG, Carvalho B, Sharkey A, Pawa A, Gadsden J. Essentials of Our Current Understanding: Abdominal Wall Blocks. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017;42(2):133-183. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000545.
- Carline L, McLeod GA, Lamb C. A cadaver study comparing spread of dye and nerve involvement after three different quadratus lumborum blocks. Br J Anaesth. 2016;117(3):387-94. doi: 10.1093/bja/aew224.
- Dam M, Moriggl B, Hansen CK, Hoermann R, Bendtsen TF, Børglum J. The Pathway of Injectate Spread With the Transmuscular Quadratus Lumborum Block: A Cadaver Study. Anesth Analg. 2017;125(1):303-312. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001922.
- Hassanein A, Abdel-Haleem M, Mohamed SR. Regional Analgesia for Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Using Ultrasound-guided Quadratus Lumborum Block or Erector Spinae Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Physician. 2023;26(3):E133-E141.
- Kulhari S, Shamshery C, Ambasta S, Agarwal A, Singh RK, Srivastava M. Postoperative analgesic efficacy of quadratus lumborum block in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study. Indian J Pain. 2022;36(1):33-36. doi: 10.4103/ijpn.ijpn_92_21.
- Ökmen K, Metin Ökmen B, Topal S. Ultrasound-guided posterior quadratus lumborum block for postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A randomized controlled double blind study. J Clin Anesth. 2018;49:112-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2018.06.027.
- Ökmen K, Metin Ökmen B, Sayan E. Ultrasound-guided lateral versus posterior Quadratus Lumborum Block for postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled trial. Turk J Surg. 2019;35(1):23-29. doi: 10.5578/turkjsurg.4161.
- Baytar Ç, Yılmaz C, Karasu D, Topal S. Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block and Quadratus Lumborum Block in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Study. Pain Res Manag. 2019;2019:2815301. doi: 10.1155/2019/2815301.