Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 59, №3, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Гіперлептинемія у хворих на гастроезофагеальну рефлюксну хворобу та ожиріння: підходи до оцінки та профілактики лептинорезистентності
Авторы: Мосійчук Л.М., Татарчук О.М., Кленіна І.А., Шевцова О.М., Петішко О.П.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
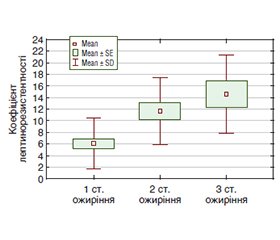
Актуальність. Гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба (ГЕРХ) та ожиріння залишаються найбільш поширеною коморбідною патологією, яка суттєво впливає на погіршення якості життя пацієнтів. Багато досліджень проведено для визначення факторів, що сприяють розвитку цих захворювань, проте найбільш дискутабельним залишається питання ролі лептину. На сьогодні немає чітких критеріїв для ефективної оцінки чутливості до лептину в клінічних умовах, хоча окремі дослідники вважають гіперлептинемію ключовим маркером лептинорезистентності. Мета: обґрунтувати підходи до оцінки та профілактики лептинорезистентності у пацієнтів із ГЕРХ та ожирінням. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 60 чоловіків, хворих на ГЕРХ та ожиріння, які були розподілені на три групи залежно від рівня лептину. Усім хворим в сироватці крові визначали рівні фактора некрозу пухлини альфа, інтерлейкіну 6 (ІЛ-6), лептину, інсуліну, вміст загального холестерину, тригліцеридів (ТГ), холестерину ліпопротеїнів високої щільності, а також розраховували холестерин ліпопротеїнів низької щільності, холестерин ліпопротеїнів дуже низької щільності (ЛПДНЩ), коефіцієнт атерогенності та коефіцієнт інсулінорезистентності (HOMA-IR). Для оцінки тривожного синдрому та виснаженості організму застосовували Precise-діагностику на кардіографі CONTECT 8000GW. Аналіз складу тіла проводили з використанням вагів-аналізаторів TANITA МС-780МА (Японія). Результати. У 38,2 % хворих з гіперлептинемією діагностований тривожний синдром, у 52,9 % — виснаженість організму, у 44,1 % — порушення сну, у 64,7 % — небезпечну кількість вісцерального жиру. Виявлено прямі кореляційні зв’язки лептину з гіперінсулінемією (r = 0,316; р = 0,015), інсулінорезистентністю (r = 0,302; р = 0,020), збільшенням рівня ТГ (r = 0,414; р = 0,003), ЛПДНЩ (r = 0,381; р = 0,006) та ІЛ-6 (r = 0,507; р < 0,001). Для оцінки лептинорезистентності застосовували коефіцієнт співвідношення рівня лептину та рівня тригліцеридів, який у хворих на ГЕРХ з 1 ступенем ожиріння становив (6,07 ± 0,81) ум.од., з 2 ступенем ожиріння — (11,64 ± 1,44) ум.од., з 3 ступенем ожиріння — (14,54 ± 2,26) ум.од. (F = 11,67; р < 0,0001). При наявності небезпечної кількості вісцерального жиру коефіцієнт лептинорезистентності збільшувався в 1,6 раза порівняно з хворими на ГЕРХ із безпечним рівнем вісцерального жиру (t = 2,80; р = 0,008). Інсулінорезистентність асоціювалася зі значним підвищенням коефіцієнта лептинорезистентності — у 2,5 раза (t = 4,98; р < 0,0001). За результатами регресійного аналізу визначено, що значення коефіцієнта співвідношення лептину та рівня тригліцеридів понад 8,43 ум.од. з чутливістю 62,9 % та специфічністю 96,0 % можна використовувати як малоінвазивний маркер оцінки лептинорезистентності. Висновки. Обґрунтовані підходи до оцінки та профілактики лептинорезистентності у хворих на ГЕРХ та ожиріння сприятимуть підвищенню ефективності лікувальних заходів.
Background. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and obesity remain the most common comorbid pathology, which significantly affects the deterioration of the quality of life of patients. Many studies have been conducted to determine the factors contributing to the development of these diseases, but the role of leptin remains the most debatable issue. Currently, there are no clear criteria for effective assessment of leptin sensitivity in clinical settings, although some researchers consider hyperleptinemia to be a key marker of leptin resistance. The aim is to substantiate approaches to the assessment and prevention of leptin resistance in patients with GERD and obesity. Materials and methods. Sixty men with GERD and obesity were examined and divided into three groups depending on the leptin level. All patients had serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6, leptin, insulin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, atherogenic index and insulin resistance index calculated. To assess anxiety syndrome and body exhaustion, precise diagnostics was used on the CONTEC 8000GW cardiograph. Body composition analysis was performed using TANITA MC-780MA scale analyzers (Japan). Results. 38.2 % of patients with hyperleptinemia were diagnosed with anxiety syndrome, 52.9 % with exhaustion, 44.1 % with sleep disorders, and 64.7 % had a dangerous amount of visceral fat. Direct correlations of leptin with hyperinsulinemia (r = 0.316; p = 0.015), insulin resistance (r = 0.302; p = 0.020), increased levels of triglycerides (r = 0.414; p = 0.003), very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (r = 0.381; p = 0.006) and interleukin 6 (r = 0.507; p < 0.001) were found. To assess leptin resistance, the ratio of leptin to triglyceride level was used, which in patients with GERD with degree 1 obesity was (6.07 ± 0.81) conventional units, with degree 2 obesity — (11.64 ± 1.44) conventional units, with degree 3 obesity — (14.54 ± 2.26) conventional units (F = 11.67; p < 0.0001). In the presence of a dangerous amount of visceral fat, the leptin resistance coefficient increased by 1.6 times compared to patients with GERD with a safe level of visceral fat (t = 2.80; p = 0.008). Insulin resistance was associated with a significant increase in the leptin resistance coefficient — by 2.5 times (t = 4.98; p < 0.0001). According to the results of regression analysis, it was found that the ratio of leptin to triglyceride level above 8.43 conventional units with a sensitivity of 62.9 % and a specificity of 96.0 % can be used as a minimally invasive marker for assessing leptin resistance. Conclusions. Reasoned approaches to the assessment and prevention of leptin resistance in patients with GERD and obesity will contribute to increasing the effectiveness of treatment measures.
гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба; ожиріння; гіперлептинемія; ліпідний та вуглеводний обмін; лептинорезистентність
gastroesophageal reflux disease; obesity; hyperleptinemia; lipid and carbohydrate metabolism; leptin resistance
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Quality of life and severity of symptoms among patients with va–rious degrees of reflux esophagitis: a prospective study / A. Mari et al. Sci Rep. 2023. Vol. 13(1). P. 13970. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41332-w.
- Azer S.A., Goosenberg E. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; July 6, 2025.
- Seeras K., Campbell J., Pryor A.D. Considerations in the ma–nagement of gastroesophageal reflux disease in the morbidly obese. Ann Esophagus 2022. Vol. 5. P. 41. doi: 10.21037/aoe-21-20.
- Relationship of different metabolic obesity phenotypes with reflux esophagitis: a propensity score matching analysis / T. He et al. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. Vol. 24(1). P. 239. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01771-6.
- He T., Sun X., Duan Z. Nomogram for predicting reflux esopha–gitis with routine metabolic parameters: a retrospective study. Arch Med Sci. 2024. Vol. 20(4). P. 1089-1100. doi: 10.5114/aoms/175536.
- Inflammatory mediators in gastroesophageal reflux disease: impact on esophageal motility, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis / F. Rieder et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. Vol. 298. P. G571-81.
- Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication / M. Obradovic et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. Vol. 12. P. 585887. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.585887.
- Münzberg H., Heymsfield S.B., Berthoud H.R., Morrison C.D. History and future of leptin: Discovery, regulation and signaling. Metabolism: clinical and experimental. 2024. Vol. 161. P. 156026. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2024.156026.
- Associations of diabetes mellitus, insulin, leptin, and ghrelin with gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett’s esophagus / J.H. Rubenstein et al. Gastroenterology. 2013. Vol. 145(6). P. 1237-44. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.052.
- Бондар-Келеберда О. Роль греліну та лептину у формуванні морфологічних змін стравоходу пацієнтів з гастроезофагеальною рефлюксною хворобою на тлі діабету 2 типу. EUREKA: Health Sciences. 2023. № 4. С. 24-33. doi: 10.21303/2504-5679.2023.003276.
- Novel mechanisms involved in leptin sensitization in obesity / V. Pena-Leon et al. Biochemical pharmacology. 2024. Vol. 223. P. 116129. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116129.
- Association between Leptin (G2548A) and Leptin Receptor (Q223R) Polymorphisms with Plasma Leptin, BMI, Stress, Sleep and Eating Patterns among the Multiethnic Young Malaysian Adult Population from a Healthcare University / J. Mohanraj et al. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2022. Vol. 19(14). P. 8862. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148862.
- Suriagandhi V., Nachiappan V. Protective Effects of Melatonin against Obesity-Induced by Leptin Resistance. Behavioural brain research. 2022. Vol. 417. P. 113598. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113598.
- Ghadge A.A., Khaire A.A. Leptin as a predictive marker for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine. 2019. Vol. 121. P. 154735. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154735.
- Relationship between nutritional treatment compliance and nutritional status improvements in patients with gastrointestinal impairment taking an oral peptide-based supplement / J.A. López-Medina et al. Nutrition. 2022. Vol. 102. P. 111734. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2022.111734.
- Engin A. The Mechanism of Leptin Resistance in Obesity and Therapeutic Perspective. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2024. Vol. 1460. P. 463-487. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_16.
- Liu Y., Gong F. Natural Products From Plants Targeting Leptin Resistance for the Future Development of Anti-Obesity Agents. Phytotherapy research. 2025. Vol. 39(2). P. 1174-1189. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8415.
- Münzberg H., Heymsfield S.B. Leptin, obesity, and leptin resistance. In: Dagogo-Jack S, editor. Leptin. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2015. P. 67-78.
- Яринич Ю.М. Роль адипоцитокінів у розвитку неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки у хворих на артеріальну гіпертензію й ожиріння. Міжнародний ендокринологічний журнал. 2018. Т. 14. №4. С. 339-343. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.14.4.2018.140187.
- Masood M., Low D., Deal S.B., Kozarek R.A. Gastroeso–phageal Reflux Disease in Obesity: Bariatric Surgery as Both the Cause and the Cure in the Morbidly Obese Population. J Clin Med. 2023. Vol. 12(17). P. 5543. doi: 10.3390/jcm12175543.
- Abdominal obesity increases the risk of reflux esophagitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis / J. Zhan et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2022. Vol. 57(2). P. 131-142. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2021.1994643.
- The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of appetite in obesity / K. Skoracka et al. Peptides. 2025. Vol. 186 (2025). P. 171367. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2025.171367.
- Скибчик В.А., Скибчик Я.В. Проблема лептинемії при серцево-судинних захворюваннях. Український медичний часопис. 2007. T. XI/XII. № 6(62). С. 45-51. URL: www.umj.com.ua/uk/publikatsia-106-problema-leptinemii-pri-sercevo-sudinnix-zaxvoryuvannyax.
- Chang M.L., Yang Z., Yang S.S. Roles of Adipokines in Digestive Diseases: Markers of Inflammation, Metabolic Alteration and Disease Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. Vol. 21(21). P. 8308. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218308.
- Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier / W.A. Banks et al. Diabetes. 2004. Vol. 53(5). P. 1253-1260. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.5.1253.