Международный эндокринологический журнал 4 (68) 2015
Вернуться к номеру
The prevalence of carbohydrate disorders in urban population of Ukraine depending on the degree and type of obesity
Авторы: Mitchenko O.I. - SI NSC "M.D. Strazhesko Institute of cardiology, NMAS of Ukraine"; Mammedov M.N. - "State Research Center for Preventive Medicine," The Ministry of Health, Moscow; Kolesnik T.V. - "Dnepropetrovsk Medical Academy" The Ministry of Health, Ukraine, Dnipropetrovsk; Deev A.D. - "State Research Center for Preventive Medicine," The Ministry of Health, Moscow; Romanov V.Y. ., Kulyk O.Y. ., Shkreba A. A. - SI NSC "M.D. Strazhesko Institute of cardiology, NMAS of Ukraine"; on behalf of the Working Group of the Russian-Ukrainian research of 20 risk factors in Dnipropetrovsk.
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, prevalence, overweight, obesity.
Purpose: Subanalysis of the prevalence and detection of carbohydrate disorders among the cohort of respondents with overweight and obesity, depending on the degree and type of obesity in a large population within the definition of risk factors in our research of Ukraine on urban population in 2009-2013.
Methods: The study protocol included the definition and evaluation of the 20 factors of cardiovascular risk of 1000 respondents (468 men and 532 women) at the age 30-69 years living in 5 regions of Dnipropetrovsk and subanalysis contained in this publication concerned the prevalence and detection of carbohydrate disorders, depending on the degree and type of obesity. The following methods were used in this research: body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), fast levels glucose, insulin, with definition of an index of HOMA.
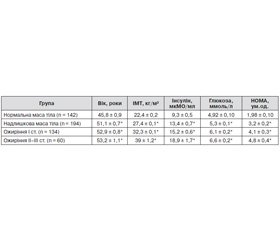
Results: According to the study of carbohydrate disorders prevalence was 77.2% among the urban population of Ukraine. Among them, insulin resistance was found in 41.2% of respondents, impaired glucose tolerance in 28%, diabetes prevalence was 8% of the population We analyzed the prevalence of carbohydrate disorders in urban populations depending on body weight and age. Among surveyed with normal body weight (291 people), insulin resistance was diagnosed in 49 respondents is 16.8%. Thus,the respondents in the age group of 30-39 years, which included 97 people, 18 found insulin resistance, which is 18.6%; at the age of 40-49 years, which included 65 respondents in 9 found insulin resistance, which is 13.9%; in the age group 50-59 years, which consisted of 90 people, 17 diagnosed insulin resistance, which is 18.9% and in the age group 60-69 years, which included 39 people, insulin resistance was diagnosed in 5, which is 12,8%.
Among those overweight (383 respondents) in 147 (38.4%) identified insulin resistance.
Respondents in the 30-39 age group, which included 90 people, 40 found insulin resistance, which is 44.4%; at the age of 40-49 years, which included 95 respondents, insulin resistance was found in 32, which is 33.7%; in the age group 50-59 years, which included 130 people - 47 found insulin resistance, which is 36.4% and in the age of 60-69 years, which included 68 people found in insulin resistance 28 people, which is 40.6 %.
Among people with obesity I degree (234 respondents), 144 (61.5% ) identified insulin resistance. Respondents with obesity and degree in the age group 30-39, which included 40 people, insulin resistance was found in 23 respondents, which is 57.5%; at the age of 40-49 years, which included 49 respondents insulin resistance was found in 23 individuals is 46%; in the age group 50-59 years, which came 101 respondents, 70 identified insulin resistance, which is 68.6%, and at the age of 60-69 years, which consisted of 45 people, insulin resistance was found in 68.9%. Among people with obesity II-III degree (92 respondents), 71 (77,2%) identified insulin resistance. Respondents in the 30-39 age group, which included 14 people, 10 found insulin resistance, which is 71.4%; aged 40-49, which included 21 people, insulin resistance was found in 15, which is 71.4%; in the age group 50-59 years, which consisted of 41 people in 31 found insulin resistance, which is 75.6%, and at the age of 60-69, which included 16 respondents, 15 identified insulin resistance, which is 93.8% . A similar analysis conducted on the basis of gender differences, and in groups of overweight and different degrees of obesity. We analyzed the detection of hypertension in urban population Ukraine according to the type of obesity. The results were analyzed according to the type of abdominal obesity defined by the criteria AНA (2013) and ESC (2012).
Conclusions: We have determined that in the analyzed urban population of Ukraine's population had a normal body weight only 29.3% of the population and 70.7% had total overweight and obesity I-III degree, and the total prevalence of carbohydrate disorders in the population was 77.2 %. Discovered that an increase in body weight, insulin resistance detection rate increased from 16.8% at normal body weight to 77.2% for obesity II-III degree, the percentage of violations of tolerance to glucose increased from 23.4% in normal weight body to 36.9% for obesity II-III degree and percentage detection of diabetes from 3.4% to 16.3% respectively. It is established that the occurrence of abdominal type of obesity in men accompanied by deepening disorders of carbohydrate disorders and growth detect insulin resistance to 35,4%, impaired glucose tolerance by 5.6%, diabetes by 8.3% against men without evidence of abdominal obesity. In women, the appearance of abdominal obesity associated with growth only detect insulin resistance 7.8% and 5.0% impaired glucose tolerance against women without evidence of abdominal obesity.