Международный эндокринологический журнал 7 (71) 2015
Вернуться к номеру
Инсулин Тожео — новый базальный инсулин длительного действия Часть 1. Фармакокинетический и фармакодинамический аспекты
Авторы: Полторак В.В., Кравчун Н.А. - ГУ «Институт проблем эндокринной патологии им. В.Я. Данилевского НАМН Украины», г. Харьков; Горшунская М.Ю. - Харьковская медицинская академия последипломного образования
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
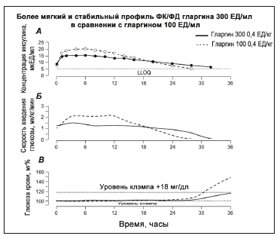
В данном обзоре, состоящем из двух частей, рассматривается новая формула инсулина гларгин (рДНК происхождения) в форме инъекций 300 ЕД/мл (Gla-300, Тожео). Gla-300 представляет следующую генерацию базального инсулина с новой формулой инсулина гларгин, поставляющего то же количество инсулина, что и гларгин-100 (Gla-100, Лантус®) в 1/3 объема. После подкожной инъекции фармакокинетический и фармакодинамический профили Gla-300 являются более постоянными и продолжительными (более 24 часов) по сравнению с Gla-100, что обусловлено более постепенным и длительным выделением гларгина из подкожного депо (Gla-300 образует более компактное подкожное депо с уменьшенной поверхностью по сравнению с Gla-100). С акцентом на недавних результатах клинических исследований EDITION (3а-фаза) обсуждается клиническая эффективность и безопасность Gla-300 у больных сахарным диабетом 1-го и 2-го типа. Gla-300 демонстрировал сопоставимый гликемическиий контроль и подобный профиль безопасности при условиях более низкой частоты гипогликемических событий по сравнению с Gla-100. Gla-300 обеспечивал гибкий режим введения инсулина (24 ± 3 часа или утром vs вечером) и был ассоциирован с меньшим увеличением массы тела.
В цьому огляді, що складається з двох частин, розглядається нова формула інсуліну гларгін (рДНК походження) у формі ін’єкцій 300 ОД/мл (Gla-300, Тожео). Gla-300 являє собою наступну генерацію базального інсуліну з новою формулою інсуліну гларгін, що поставляє ту ж кількість інсуліну, як і гларгін-100 (Gla-100, Лантус®) в 1/3 об’єму. Після підшкірної ін’єкції фармакокінетичний та фармакодинамічний профілі Gla-300 є більш постійними та тривалими (більше ніж 24 години) порівняно з Gla-100, що пов’язано з більш поступовим та тривалим виділенням гларгіну із підшкірного депо (Gla-300 утворює більш компактне підшкірне депо зі зменшеною поверхнею порівняно з Gla-100). З акцентом на недавніх результатах клінічних досліджень EDITION (3а-фаза) обговорюється клінічна ефективність та безпечність Gla-300 у хворих на цукровий діабет 1-го та 2-го типу. Gla-300 демонстрував порівнянний глікемічний контроль та подібний профіль безпечності за умов більш низької частоти гіпоглікемічних подій порівняно з Gla-100. Gla-300 забезпечував гнучкий режим введення інсуліну (24 ± 3 години або ранком vs вечером) та був асоційований iз меншим збільшенням ваги.
This review, consisting of two parts, considers a new formulation of insulin glargine (rDNA origin) in the form of injections 300 U/ml (Gla-300, Toujeo®). Gla-300 is a next generation basal insulin with a novel formulation of insulin glargin delivering the same amount of insulin, as glargine-100 (Gla-100, Lantus®) in 1/3 volume. Following the subcutaneous injection, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of Gla-300 are more constant and prolonged (beyond 24 hours) compared with Gla-100 due to a more gradual and extended release of glargine from subcutaneous depot (Gla-300 forms a more compact subcutaneous depot with reduced surface area compared to Gla-100). The clinical efficacy and safety of Gla-300 in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus are discussed with an emphasis on recently released data from EDITION (the phase 3a) clinical trials. Gla-300 showed comparable glycaemic control and similar safety profile with lower incidence of hypoglycaemia events compared with Gla-100. Gla-300 provided flexible dosing of insulin (24 ± 3 h or morning vs evening) and was associated with less body weight gain.
сахарный диабет, гликированный гемоглобин, гипогликемия, гларгин, инсулин, Gla-100 (Лантус®), Gla-300 (Тожео).
цукровий діабет, глікований гемоглобін, гіпоглікемія, гларгін, інсулін, Gla-100 (Лантус®), Gla-300 (Тожео).
diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin, hypoglycaemia, glargine, insulin, Gla-100 (Lantus®), Gla-300 (Toujeo®).
Статья опубликована на с. 22-35
Введение
Фармакокинетика, фармакодинамика и метаболизм
Глоссарий (для обеих частей обзора)
(для обеих частей обзора)
1. Ahsen B. Avoiding hypoglycemia: a key to success for glucose-lowering therapy in type 2 diabetes // Vasc. Healht. Risk. Man. — 2013. — Vol. 9. — P. 155-163.
2. American Diabetes Association. Standarts of medical care in diabetes — 2014 // Diabetes Care. — 2014. — Vol. 37. — P. S14-S80.
3. Andrews M.A., O’Malley P.G. Diabetes overtreatment in eldery individuals: risky business in need of better management // JAMA. — 2014. — Vol. 311. — P. 2326-2327.
4. Approval package for application number NDA 21-081/S-024, 2007. [Electronic resourse]. — Available from: www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2007/0210810 rig1s024.pdf
5. Arnolds S., Kuglin B., Kapitza C. et al. How pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles pave the way for optimal basal insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes // Int. J. Clin. Pract. — 2010. — Vol. 64. — P. 1415-1424.
6. Atkinson M.A., Eisenbarth G.S., Michels A.W. Type 1 diabetes // Lancet. — 2014. — Vol. 383. — P. 69-82.
7. Atkinson M.A., George S., Eisenbarth G.S. 1947–2012 // Diabetologia. — 2013. — Vol. 56. — P. 435-438.
8. Atkinson M.A., Herrath M., Powers A.C., Clare-Salzer M. Current concepts of the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes — consi-derations for attempts to prevent and reverse the disease // Diabetes Care. — 2015. — Vol. 38 — P. 979-988.
9. A Trial Comparing Cardiovascular safety of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in subjects with type 2 diabetes at high risk of cardiovascular events (DEVOTE). ClinicalTrials.gov; US National Institutes of Health. [Electronic resourse]. — Available from: http//www.clinicaltrial.gov/ct2/show/NTC01959529?term-devote+degludec&rank=1.
10. Barlocco D. Insulin detemir. Novo Nordisk // Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. — 2003. — Vol. 4. — P. 449-454.
11. Barnett A.H. Insulin glargine in the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes // Vask. Health Risk Manag. — 2006. — Vol. 2. — P. 59-67.
12. Becker R.H.A., Hahn A.D., Boderke P. et al. 2011. European Patent Applicator Long-acting formulations of insulins. European Patent Office (Application No. 11166415.7) // Available from https://data.epo.org
13. Becker R.H.A., Nowotny I., Teichert L. et al. Low within- and between-day variability in exposure to new insulin glargine 300 U.ml-1 // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 892-P.
14. Becker R.H.A., Dahmen R., Bergmann K. et al. New insulin glargin 300 U.mL-1 provides a more even activity profile and prolonged glycemic control at steady state compared with insulin glargine 100 U.ml-1 // Diabetes Care. — 2015. — Vol. 38. — P. 637-643.
15. Bergenstal R., Bailey T., Robard D. et al. Insulin glargine 300 U/ml vs 100 U/ml: glucose profiles of morning vs evening injections in adults with T1DM measured with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) // Diabetes Technol. Ther. — 2015. — Vol. 17. — P. A16-17 (abstract 39).
16. Bergenstal R.M., Bailey T.S., Rodbard D. et al. Insulin glargine 300 U/ml vs 100 U/ml: glucose profiles of morning vs evening injections in adults with T1DM measured with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) // 50th Annual meeting of the European Association for the Study Diabetes: Vienna, Austria, 15–19 September 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 949.
17. Bergenstal R.M., Rosenstock J., Arakaki R.F. et al. A randomized controlled study of once-daily LY2605541, a novel long-acting basal insulin, versus insulin glargine in basal insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes // Diabetes Care. — 2012. — Vol. 35. — P. 2140-2147.
18. Bolli G.B., Owens D.R. Insulin glargine // Lancet. — 2000. — Vol. 356. — P. 443-445.
19. Bolli G.B., Andreoli A.M., Lucidi P. Optimizing the replacement of basal insulin in type 1 diabetes mellitus: no longer an elusive goal in the post-NPH era // Diabetes Thechnol. Ther. — 2011. — Vol. 13, Suppl. 1. — P. S43-S52.
20. Bolli G.B., Hahn A.D., Schmidt R. et al. Plasma exposure to insulin glargine and its metabolites M1 and M2 after subcutaneous injection of therapeutic and supratherapeutic doses of glargine in subjects with type 1 diabetes // Diabetes Care. — 2012. — Vol. 35. — P. 2626-2630.
21. Bolli G.B., Riddle M.C., Bergenstal R.M. et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/ml: glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in insulin-naive people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (EDITION 3) // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 947.
22. Bolli G.B., Riddle M.C., Bergenstal R.M. et al. New insulin Glargine 300 U/ml: glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in insulin naïve people with T2DM (EDITION 3) // 50th Annual meeting of the European Association for the Study Diabetes, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 September 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 947.
23. Bolli G.B., Riddle M.C., Bergenstal R. M. et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/ml compared with glargine 100 U/ml in insulin naïve people with type 2 diabetes on oral glucose-lowering drugs: a randomized controlled trial (EDITION 3) // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2015. — Vol. 17. — P. 386-394.
24. Bolli G.B., De Vries J.H. New long-acting insulin analogs: from clamp studies to clinical practice // Diabetes Care. — 2015. — Vol. 38. — P. 541-543.
25. Bron M., Marynchenko M., Yang H. et al. Hypoglycemia, treatment discontinuation, and costs in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on oral antidiabetic drugs // Postgrad. Med. — 2012. — P. 124-132.
26. Butler A.E., Galasso R., Meier J.J. et al. Modestly increased beta cell apoptosis but no increased beta cell replication in recentonset type 1 diabetic patients who died of diabetic ketoacidosis // Diabetologia. — 2007. — Vol. 50. — P. 2323-2331.
27. Calvert M.J., McManus R.J., Freemantle N. et al. Mana-gement of type 2 diabetes with multiple oral hypoglycaemic agents or insulin in primary care: retrospective cohort study // Br. J. Gen. Pract. — 2007. — Vol. 57. — P. 455-460.
28. Camprioni M., Tofolo G., Basu R. et al. Minimal model assessment of hepatic insulin extraction during an oral test from standard insulin kinetic parameters // Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. — 2009. — Vol. 297. — P. E941-E948.
29. Chapman T.M., Perry C.M. Insulin detemir: a review of its use in the management of type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus // Drugs. — 2004. — Vol. 64. — P. 2577-2595.
30. Dahmen R., Bergmann K., Lehmann A. et al. New insulin glargine U300 formulation events and prolongs steady state PK and PD profiles during euglycemic clamp in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) // Diabetes. — 2013. — Vol. 62, Suppl. 1. — P. A29.
31. Data on file-Real-World Data On Hypos following Basal Insulin Initiation (Value@Access team).
32. Davies M. The reality of glycemic control in insulin trea-ted diabetes: defining the clinical challenges // Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. — 2004. — Vol. 28, Suppl. 2. — P. S14-S22.
33. Davies M.J., Gagliardino J.J., Gray L.J. et al. Real-world factors affecting adherence to insulin therapy in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review // Diabet. Med. — 2013. — Vol. 30. — P. 512-524.
34. Deiss D., Kordonouri O., Hartmann R. Treatment with insulin glargine reduces asymptomatic hypoglycemia detected by continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes // Pediatr. Diabetes. — 2007. — Vol. 8. — P. 157-162.
35. Dorland’s illustrated medical dictionary, edition 28, W.B. Saunders company.
36. Eaton R.P., Allen R.C., Shade D.S. et al. «Normal» insulin secretion: the goal of artifical insulin delivery systems? // Diabetes Care. — 1980. — Vol. 3 — P. 270-273.
37. Eaton R.P., Allen R.C., Shade D.S. Hepatic removal of insulin in normal man: dose response to endogenous insulin secretion // J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. — 1983. — Vol. 56. — P. 1294-1300.
38. Evans M., Schumm-Draeger P.M., Vora J. et al. A review of modern insulin analogue pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles in type 2 diabetes: improvements and limitations // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2011. — Vol. 8. — P. 677-684.
39. Fagot J.P., Blotiere P.O., Ricordeau P. et al. Does insuline glargine increase the risk of cancer compared with other basal insulins? A French nationwide cohort study based on national administrative databases // Diabetes Care. — 2013. — Vol. 36. — P. 294-301.
40. Garber A.J., King A.B., Del Prato S. et al. Insulin Degludec an ultra-longating basal insulin, versus insulin glargine in basal bolus treatment with mealtime insulin apart in type 2 diabetes (BEGIN Basal-Bolus Type 2): a phase 3, randomized open-label, treat-to-target non-inferiority trial // Lancet. — 2012. — Vol. 379. — P. 1498-1507.
41. Gerstein H.C., Bosch J., Dagenais G.R. et al. ORIGIN Trial Investigators. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycemia // N. Engl. J. Med. — 2012. — Vol. 367. — P. 319-328.
42. Gough S.C., Harris S., Woo V. et al. Insulin degludec: overview of a novel ultra long-acting basal insulin // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2013. — Vol. 15. — P. 301-309.
43. Goykhman S., Drincic A., Desmangles J.C. et al. Insulin glargine a review 8 years after its introduction // Expert Opin. Pharmacother. — 2009. — Vol. 10. — P. 705-718.
44. Grimaldi-Bensouda L., Cameron D., Marty M. et al. Risk of breast cancer by individual insulin use: an international multicenter study // Diabetes Care. — 2014. — Vol. 37. — P. 134-143.
45. Gualandi-Signorini A.M., Giorgi G. Insulin formulations — a review // Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. — 2001. — Vol. 5. — P. 73-83.
46. Heise T., Nosek L., Bottcher S.G. et al. Ultra-long-acting insulin degludec has a flat and stable glucose-lowering effect in type 2 diabetes // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2012. — Vol. 14. — P. 944-950.
47. Heller S., Koenen C., Bode B. Comparison of insulin glargine in a basal-bolus regimen, with insulin aspart as the mealtime insulin, in patients with type 1 diabetes a 52-week, multinational, randomized open-label, parallel group, treat-to-target, noninferiority trial // Clin. Ther. — 2009. — Vol. 31. — P. 2086-2097.
48. Henricksen J.H., Tronier B., Bülow J.B. Kinetics of circulating endogenous insulin, C-peptide, and proinsulin in fasting nondiabetic man // Metabolism. — 1987. — Vol. 36. — P. 463-468.
49. Hilgenfeld R., Seipke G., Berchold H. et al. The evolution of insulin glargine and its continuing contribution to diabetes care // Drugs. — 2014. — Vol. 74. — P. 911-927.
50. Hirsh I.B., Bergenstal R.M., Parkin Ch.G. et al. A Real-World Approach to Insulin Therapy in Primary Care Practice // Clin. Diabetes. — 2005. — Vol. 23. — P. 78-86.
51. Hollander P., Cooper J., Bregnhoi J. et al. A 52-week, multinational open-label parallel-group noninferiority treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with insulin glargine in a basal-bolus regimen with mealtime insulin aspart in patients with type 2 diabetes // Clin. Ther. — 2008. — Vol. 30. — P. 1976-1987.
52. Holman R.R., Farmer A.J., Davies M.J. et al. Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes // N. Engl. J. Med. — 2009. — Vol. 361. — P. 1736-1747.
53. Home P.D., Bergenstal R.M., Riddle M.C. et al. Glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia with new insulin Glargine 300 U/mL in people with type 1 diabetes (EDITION 4) // Diabetologia. — 2014. — Vol. 57, Suppl. 1. — P. S69.
54. Home P.D., Bergenstal R.M., Riddle M.C. et al. Glycemic control and hypoglycemia with new insulin glargine 300 U/ml in people with T1DM (EDITION 4) // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 80-LB.
55. Home P.D., Bergenstal R.M., Bolli G.B. et al. New insulin glargine 300Units/ml versus glargine 100 Units/mL in people with type 1 diabetes: a randomized, phase 3a, open-label clinical trial (EDITION 4) // Diabetes Care. — 2015 Publish Ahead of Print.
56. Hopkins D. Exercise-induced and other daytime hypoglycemic events in patients with diabetes: prevention and treatment // Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. — 2004. — Vol. 65, Suppl. 1. — P. S35-S39.
57. Horvath K., Jeitler K., Berghold A. et al. Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH insulin (human isophane insulin) for type 2 diabetes mellitus // Cochane Database Syst. Rev. — 2007. — CD005613
58. Iglesias P., Diez J.J. Insulin therapy in renal disease // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2008. — Vol. 10. — P. 811-823.
59. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas. — 6th edition. — Brussels; Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2013.
60. Investigators O.T., Gerstein H.C., Bosch J. et al. Basal insulin and cardiovascular and other outcomes in dysglycaemia // N. Engl. J. Med. — 2012. — Vol. 367. — P. 319-328.
61. Inzucchi S.E., Bergenstal R.M., Buse J.B. et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) // Diabetes Care. — 2012. — Vol. 35. — P. 1364-1379.
62. Inzucchi S.E., Bergenstal R.M., Buse J.B. et al. Mana-gement of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) // Diabetes Care. — 2015. — Vol. 38. — P. 140-149.
63. Ishii H., Iwamoto Y., Tajima N. An Exploration of Barriers to Insulin Initiation for Physicians in Japan: Findings from the Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes and Needs (DAWN) JAPAN Study // Plos. One. — 2012. — Vol. 7. — P. e36361.
64. Jax J., Heise T., Dahmen R. et al. New insulin glargine formulation has a flat and prolonged steady state profile in subjects with type 1 diabetes // Diabetologia. — 2013. — Vol. 56. — P. A1029.
65. Jeandidier N., Riddle M.C., Bolli G.B. et al. New insulin Glargine 300 U/ml: efficacy and safety of flexible vs fixed dosing intervals in people with 2 diabetes mellitus // 50th Annual meeting of the European Association for the Study Diabetes, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 September 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 961.
66. Jinnouchi H., Koyama M., Amano A. et al. Continuous Glucose monitoring during basal-bolus therapy using Glargine
300 U ml-1 and Glargine 100 U ml-1 in Japanese People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Crossover pilot study // Diabetes Ther. — 2015.
67. Jørgensen K.H., Hansen A.K., Buschard K. Five fold increase of insulin concentration delays the absorption of subcutaneously injected human insulin suspensions in pigs // Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. — 2000. — Vol. 50. — P. 161-167.
68. Kuerzel G.U., Shukla U., Scholtz H.E. et al. Biotransformation of insulin glargine after subcutaneous injection in healthy subjects // Curr. Med. Res. Opin. — 2003. — Vol. 19. — P. 34-40.
69. Kuricova K., Pacal L., Kankova K. Hypoglycemia Increa-ses Expression of Several Genes Upregulated by Hyperglycemia // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 401-P.
70. Lambert P.C., Sutton A.J., Abrams K.P., Jones D.R. A comparison of summary patient-level covariates in meta-regression with individual patient data meta-analysis // J. Clin. Epidemiol. — 2002. — Vol. 55. — P. 86-94.
71. Lamy A., Tong W., Jung H. et al. Cost implications of the use of basal insulin glargine in people with early dysglycemia: the ORIGIN trial // J. Diabetes Complications. — 2014. — Vol. 28. — P. 553-558.
72. Leese G.P.,Wang J., Broomhall J. et al. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia requiring emergency treatment in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a population-based study of health service resource use // Diabetes Care. — 2003. — Vol. 26. — P. 1176-1180.
73. Leiter L.A., Yale J.-F., Chiasson J.-L. et al. Assessment of the impact of fear of hypoglycemic episodes on glycemic and hypoglycemia management // Can. J. Diabetes. — 2005. — Vol. 29. — P. 186-192.
74. Lucidi P., Porcellati F., Candeloro P. et al. Glargine metabolism over 24 h following its subcutaneous injection in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a dose-response study // Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. — 2014. — Vol. 24. — P. 709-716.
75. Mannucci E., Giannini S., Dicembrini I. Cardiovascular effects of basal insulins // Drugs, healthcare and patient safety. — 2015. — Vol. 7. — P. 113-120.
76. Markussen J., Diers I., Hougaard P. et al. Soluble, prolonged-acting insulin derivatives. III. Degree of protraction, crystallizability and chemical stability of insulins substituted in positions A21, B13, B23, B27 and B30 // Protein Eng. — 1988. — Vol. 2. — P. 157-166.
77. Martens G.A., Van de Casteele M. Glycemic control of apoptosis in the pancreatic beta cell: danger of extremes? // Antioxid. Redox. Sygnal. — 2007. — Vol. 9. — P. 309-317.
78. Matsuhisa M., Koyama M., Cheng X. et al. EDITION JP 1 Study Group. New insulin Glargine 300 U/ml: glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in Japanese people with T1DM (EDITION JP 1) //
50th Annual meeting of the European Association for the Study Diabetes, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 September 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 975.
79. Matsuhisa M., Koyama M., Cheng X. et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/mL: glycemic control and hypoglycemia in Japanese people with T1DM (EDITION JP I) // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 88-LB.
80. Matsuhisa M., Koyama M., Cheng X. et al. Sustained glycemic control and less nocturnal hypoglycemia with new insulin glargine 300 U/mL compared with glargine 100 U/mL over 12 months in Japanese people with T1DM (EDITION JP 1) on behalf of the EDITION JP 1 study group // 75th Scientific sessions of ADA, Boston, USA, 5–9 June 2015. — 2015. — Abstract 987-P.
81. Meier J.J. Beta cell mass in diabetes: a realistic therapeutic target? // Diabetоlogia. — 2008. — Vol. 51. — P. 703-713.
82. Mellbin L.G., Ryden L., Riddle M.C. et al. Does hypoglycaemia increase the risk of cardiovascular events? A report from the ORIGIN trial // Eur. Heart. J. — 2013. — Vol. 34. — P. 3137-3144.
83. Monami M., Adalsteinsson J.E., Desireri C.M. et al. Fas-ting and post-prandial glucose and diabetic complication. A meta-analysis // Nurt. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. — 2013. — Vol. 23. — P. 591-598.
84. Monti L.D., Poma R., Caumo A. et al. Intravenous infusion of diarginylinsulin, an insulin analogue: effects on glucose turnover and lipid levels in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients // Metabolism. — 1992. — Vol. 41. — P. 540-544.
85. Mullins P., Sharplin P.,Yki-Jarvinen H. et al. Negative binomial meta-regression analysis of combined glycosylated hemoglobin and hypoglycemia outcomes across eleven Phase III and IV studies of insulin glargine compared with neutral Hagedorn insulin in type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus // Clin. Ther. — 2007. — Vol. 29. — P. 1607-1619.
86. Nieuwesteeg A., Pouwer F., van der Kamp R. et al. Quality of life of children with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review // Curr. Diabetes Rev. — 2012. — Vol. 8. — P. 434-443.
87. Nolan C.J., Damm P., Prentki M. Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management // Lancet. — 2011. — Vol. 378. — P. 169-181.
88. Owens D.R. Insulin preparations with prolonged effect // Diabetes Technol. Ther. — 2011. — Vol. 13, Suppl. 1. — P. S5-S14.
89. Owens D.R., Matfin G., Monnier L. Basal insulin analogues in the management of diabetes mellitus: what progress have we made? // Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. — 2014. — Vol. 30. — P. 104-119.
90. Peyrot M., Barnett A.H., Meneghini L.F. et al. Insulin adherence behaviors and barriers in the multinational global attitudes of patients and physicians in insulin therapy study // Diabet. Med. — 2012. — Vol. 29. — P. 682-689.
91. Pieber T.R., Treichel H.C., Hompresch B. et al. Comparison of insulin detemir and insulin glargine in subjects with type 1 diabetes using intensive insulin // Diabet. Med. — 2007. — Vol. 24. — P. 635-642.
92. Polonsky W.H., Fisher L., Guzman S. et al. Pshychological insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes: the score of the problem // Diabetes Care. — 2005. — Vol. 28. — P. 2543-2545.
93. Pontiroli A.E., Miele L., Morabito A. Increase of body weight during the first year of intensive insulin treatment in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2011. — Vol. 13. — P. 1008-1019.
94. Porcellati F., Rossetti P., Busciantella RN. et al. Comparison of Pharmacokinetics and Dynamics of the Long-Acting Insulin Analogs Glargine and Detemir at Steady State in Type 1 Diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study // Diabetes Care. — 2007. — Vol. 30. — P. 2447-2452.
95. Porcellati F., Lucidi P., Cioli P. et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin glargine given in the evening as compared with in the morning in type 2 diabetes // Diabetes Care. — 2015. — Vol. 38. — P. 503-512.
96. Raskin P., Gylvin T., Weng W. et al. Comparison of insulin detemir and insulin glargine using a basal-bolus regimen in a randomized, controlled clinical study in patients with type 2 diabetes // Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. — 2009. — Vol. 25. — P. 542-548.
97. Ratner R.E., Hirsch I.B., Neifing J.L. et al. Less hypoglycemia with insulin Glargine in intensive insulin therapy for type 1 diabetes. US Study Group of insulin Glargine in type 1 diabetes // Diabetes Care. — 2000. — Vol. 23. — P. 639-643.
98. Ricci C., Pastukh V., Mozafarri M., Shaffer S.W. Insulin withdrawal induces apoptosis via a free radical mediated mechanism // Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. — 2007 — Vol. 85. — P. 455-464.
99. Riddle M.C., Bolli G.B., Yki-Jarvinen H. et al. Sustained glycemic control and hypoglycemia with new insulin glargine 300 U/mL compared with 100 U/ml: one-year results in people with T2DM using basal + mealtime insulin (EDITION 1) // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 81-LB.
100. Riddle M.C., Bolli G.B., Home P.D. et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/ml: efficacy and safety of adaptable vs fixed dosing intervals in people with T2DM // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 919-P.
101. Riddle M.C., Bolli G.B., Ziemen M. et al. New insulin glargine 300 units/ml versus glargine 100 Units/ml in people with type 2 diabetes using basal and mealtime insulin: glucose control and hypoglycemia in a 6-month randomize controlled trial –(EDITION 1) // Diabetes Care. — 2014. — Vol. 37. — P. 2755-2762.
102. Ritzel R., Rousell R., Bolli G. et al. New insulin Glargine 300 U/ml: glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in a meta-analysis of phase 3a EDITION Clinical trials in people with T2DM // 50th Annual meeting of the European Association for the Study Diabetes, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 September 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 963.
103. Ritzel R., Roussel R., Bolli G. et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/ml: glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in a meta-ana-lysis of phase 3a EDITION clinical trials in people with T2DM // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 90-LB.
104. Ritzel R., Roussel R., Bolli G.B. et al. Patient-level meta-analysis of the EDITION 1, 2 and 3 studies: glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia with new insulin glargine 300 U/ml versus glargine 100 U/ml in people with type 2 diabetes // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2015. — Vol. 9. — P. 859-867.
105. Ritzel R., Roussel R., Giaccari A. et al. Glycemic control and hypoglycemia with insulin glargine 300 U/mL (Gla-300) vs glargine 100 U/mL (Gla-100) in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in a patient-level meta-analysis of 1-year phase 3a EDITION studies // 75th Scientific sessions of ADA, Boston, USA, 5–9 June 2015. — 2015. — Abstract 1030-P.
106. Rosenstock J., Dailey G., Massi-Benedetti M. et al. Reduced hypoglycemia risk with insulin glargine: a meta-analysis comparing insulin glargine with human NPH insulin in type 2 diabetes // Diabetes Care. — 2005. — Vol. 28. — P. 950-955.
107. Rosenstock J., Davies M., Home P.D. et al. A randomized, 52-week, treat-to-target trial comparing insulin detemir with type 2 diabetes // Diabetologia. — 2008. — Vol. 51. — P. 408-416.
108. Roussel R., d’Emden M. C., Fisher M. et al. Switching from twice-daily basal insulin to once-daily new insulin glargine 300 U/mL (Gla-300): an analysis in people with T2DM –(EDITION 1 and 2) // 75th Scientific sessions of ADA, Boston, USA, 5–9 June 2015. — 2015. — Abstract 1021-P.
109. Rubino A., McQuay L.J., Gough S.C., Kvasz M., Tennis P. Delayed initiation of subcutaneous insulin therapy after fai-lure of oral glucose-lowering agents in patients with Type 2 diabetes: a population-based analysis in the UK // Diabet. Med. — 2007. — Vol. 24. — P. 1412-1418.
110. Ryden L., Grant P.J., Anker S.D. et al. ESC Guidelines on diabetes, prediabetes, and cardiovascular disease developed in collaboration with EASD // Eur. Heart. J. — 2013. — Vol. 34. — P. 3035-3087.
111. Sanofi. Clinical study results. Phase I in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus 2013. [Electronic resourse]. — Avai-lable from: http://cn.sanofi.com/img/content/study/pdf2777-summary.pdf.
112. Schisano B., Tripathi G., McGee K. et al. Glucose oscillations, more than constant high glucose, induce p53 activation and a metabolic memory in human endothelial cells // Diabetologia. — 2011. — Vol. 54. — P. 1219-1226.
113. Shiramoto M., Eto T., Irie S. et al. Single-dose insulin glargine 300 U/ml provides prolonged, stable glycaemic control in Japanese and European people with type 1 diabetes // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2015. — Vol. 17. — P. 254-260.
114. Shiramoto M., Eto T., Watanabe A. et al. Single dose of new insulin glargine Gla-300 formulation has a flatter and prolonged PK/PD profile than Gla-100 in Japanese subjects with type 1 diabetes // Diabetologia. — 2013. — Vol. 56. — P. A1031.
115. Sinha V.P., Howey D.C., Choi S.L. et al. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and glucodynamics of the novel, long-acting basal insulin LY2605541 dosed once-daily in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2014. — Vol. 16. — P. 344-350.
116. Simon A.C., DeVries J.H. The future of basal insulin supplementation // Diabetes Technol. Ther. — 2011. — Vol. 13 (Suppl. 1). — P. S103-S108
117. Sommerfled M.R., Muller G., Tschank G. et al. In vitro metabolic and mitogenic signaling of insulin glargine and its metabolites // PLoS One. — 2010. — Vol. 5. — P.e9540.
118. Steinstaresser A., Schmidt R., Bergmann K. et al. Investigational new insulin glargine 300 U/ml has the same metabolism as insulin glargine 100 U/ml /research letter // Diabetes Obes. Metab. — 2014. — Vol. 16. — P. 873-876.
119. Sutton G., Minguet J., Ferrero C., Bramlage P. U300, A novel long-acting insulin formulation // Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. — 2014. — Vol. 14. — P.1849-1860.
120. Swinnen S.G., Dain M.P., Aronson R. et al. A 24-week, randomized, treat-to-target trial comparing initiation of insulin glargine once-daily with insulin detemir twice-daily in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral glucose-lowering drugs // Diabetes Care. — 2010. — Vol. 33. — P. 1176-1178.
121. Teramukai S., Matsuyama Y., Mizuno S. et al. Individual patient-level and study-level meta-analysis for investigating modifiers of treatment effect // Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. — 2004. — Vol. 34. P. 717-721.
122. Terauchi Y., Koyama M., Cheng X. et al. Glycemic control and hypoglycaemia in Japanese people with T2DM receiving New insulin Glargine 300 U/ml in combination with OADs (EDITION JP 2) // 50th Annual meeting of the European Association for the Study Diabetes, Vienna, Austria, 15–19 September 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 976.
123. Terauchi Y., Koyama M., Cheng X. et al. Glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia in Japanese people with T2DM recei-ving new insulin glargine 300 U/ml in combination with OADSs –(EDITION JP 2) // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 94-LB.
124. Tibaldi J.M. Evolution of insulin development: focus on key parameters // Adv. Ther. — 2012. — Vol. 29. — P. 590-619.
125. Tillner J.A., Bergmann K., Teichert L. et al. Euglycemic clamp profile of new insulin glargine U300 formulation in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) is different from glargine U100 // Diabetes. — 2013. — Vol. 62, Suppl. 1. — P. A234.
126. Toujeo (U300)-ePress Pack. [Electronic resourse] Value and access team. Data on file — Real-World on hypos following basal insulin initiation.
127. Tschope D., Bramlage P., Binz C. et al. Incidence and predictors of hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes — an analysis of the prospective // DiaRegis. registry. BMC Endocr. Disord. — 2012. — Vol. 12. — P. 23.
128. Twigg S.M., Escalada J., Grisoni M.-L. et al. Age, BMI, and diabetes duration: effect on glycemic control and hypoglycemia with insulin glargine 300 U/mL in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) // 75th Scientific sessions of ADA, Boston, USA, 5–9 June 2015. — 2015. — Abstract 1017-P.
129. UK Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration // Diabetologia. — 2007. — Vol. 50. — P. 1140-1147.
130. Vague P., Selam J.L., Skiele S. et al. Insulin detemir is associated with more predicable glycemic control and reduced risk of hypoglycemia than NPH-insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes on basal-bolus regimen with premeal, insulin apart // Diabetes Care. — 2003. — Vol. 26. — P. 590-596.
131. Wood J.R., Miller K.M., Maahs D.M. et al. Type 1 Diabetes exchange clinic registry do not meet American Diabetes Association or international Society for Pediatric and adolescent. Diabetes clinical guidelines // Diabetes Care. — 2013. — Vol. 36. — P. 2035-2037.
132. Workgroup on hypoglycemia, American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia // Diabetes Care. — 2005 — Vol. 28. — P. 1245-1249.
133. Xie L., Wei W., Pan C., Baser O. Real-world rates, predictors and associated costs of hypoglycemia among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin glargine: results of a pooled analysis of six retrospective observational studies // J. Med. Econ. — 2013. — Vol. 16. — P. 1137-1145.
134. Yakubovich N., Gerstein H.C. Serious cardiovascular outcomes in diabetes: the role of hypoglycemia // Circulation. — 2011. — Vol. 123. — P. 342-348.
135. Yale J-F., Aroda V. R., Charbonnel B. et al. Older people with type 2 diabetes: glycemic control and hypoglycemia risk with new insulin glargine 300 U/mL // 75th Scientific sessions of ADA, Boston, USA, 5–9 June 2015. — 2015. — Abstract 991-P.
136. Yki-Jarvinen H., Bergenstal R., Ziemen M. et al. New insulin glargine 300 U/mL versus glargine 100 U/mL in people with type 2 diabetes using oral agents and basal insulin: glucose control and hypoglycemia in a 6-month randomized controlled trial –(EDITION 2) // Diabetes Care. — 2014. — Vol. 37. — P. 3235-3243.
137. Yki-Jarvinen H., Bergenstal R.M., Bolli G.B. et al. Less nocturnal hypoglycemia and weight gain with new insulin glargine 300 U/ml compared with 100 U/ml: 1-year results in people with T2DM using basal insulin with OADs (EDITION 2) // 74th Scientific sessions of ADA, San Francisco, USA, 13–17 June 2014. — 2014. — Abstract 93-LB.
138. Zhang P., Zhang X., Brown J. et al. Global healthcare expenditure on diabetes for 2010 and 2030 // Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. — 2010. — Vol. 87. — P. 293-301.
139. Zinman B., Fulcher G., Rao P.V. et al. Insulin degludec, an ultra-long-acting basal insulin, once a day or three times a week versus insulin glargine once a day in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 16-week, randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial // Lancet. — 2011. — Vol. 377. — P. 924-931.
140. Zongas S., Patel A., Chamers J. et al. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death // N. Engl. J. Med. — 2010. — Vol. 363. — P. 1410-1418.
141. Ефимов А.С., Полторак В.В. Аутоиммунные аспекты инсулинзависимого сахарного диабета. Попытки иммунокоррекции на ранних стадиях заболевания // Пробл. эндокринологии. — 1989. — Т. 35. — С. 85-90.
142. Полторак В.В., Караченцев Ю., Горшунська I. Оптимізація глікемічного контролю у хворих на цукровий діабет новими аналогами інсуліну (фізіологічні моделі замісної інсулінотерапії) // Ліки України. — 2005. — T. 91. — C. 63-68.
143. Полторак В.В., Красова Н.С., Горшунская М.Ю. Гликемическая память как патогенетическое основание для формирования алгоритма современной антидиабетической терапии // МЭЖ. — 2014. — T. 59. — C. 15-22.
144. Полторак В.В., Красова Н.С., Горшунская М.Ю. Апоптоз панкреатических бета-клеток как новая мишень для инсулинотерапии больных сахарным диабетом 1-го и 2-го типа // Проблемы эндокринной патологии. — № 1. — 2015. — C. 90-102.
145. Препарат Тожео (Toujeo®) затверджений у Європейському союзі для лікування діабету у дорослих — новий базальний інсулін показав глікемічний контроль із меншою кількістю випадків підтвердженої гіпоглікемії // МЭЖ. — 2015. — № 3. — С. 96-98.
146. Тронько М.Д., Полторак В.В., Соколова Л.К. Дослі–дження ORIGIN (передумови, результати) // МЭЖ. — 2013. — № 1 (49). — С. 15-22.
147. Тронько Н.Д., Зак К.П., Попова В.В., Бутенко А.К. Сахарный диабет. Иммунитет. Цитокины. — К.: Книга-плюс, 2015. — 488 с.
148. Чернобровий А.Д., Тронько М.Д. Довідник основних показникiв дiяльностi ендокринологiчної служби України за 2013 рiк. — К., 2014. — 40 с.
Продолжение в следующем номере

/25.jpg)
/26.jpg)